A Review of Attempts to Identification and Antifungal Susceptibility of Dermatophytes (Microsporum Canis and Tricophyton Mentagrophytes) Isolated from Infected Cats and Dogs with Experimental Dermatophytosis of Guinea Pigs
Abstract
Dermatophytosis affect companion animal’s skin and keratin appendages as cats and dogs, resulting in red, scaly, itchy, bald, and raised patches like ring. The three main groups are Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton. This study collected samples of skin scrapping and hairs from 130 cats and 70 dogs, using common mycological approach samples were examined. Antifungal agar disc diffusion and broth microdilution assays were utilized on some of the isolates. Three groups of Guinea pigs (6 in each) were then infected with one isolate of M. canis or T. mentagrophytes fungi, another skin scrapping samples of virulent fungi was isolated on the 7th and 14th days, blood samples were collected at 14th day. Reverse transcription-PCR to detect 98 bp protease gene. Resulting in 45% of cats and dogs tested positive for Microsporum and Trichophyton species. Agar disc diffusion revealed that the antifungal medication griseofulvin was the most effective against tested isolates. The best results for MIC test were griseofulvin (0.98 µg/ml) followed by acetic acid (0.28 µg/ml). Differential leukocytic count of Guinea pigs showed that monocyte levels remained unchanged, while neutrophil and lymphocyte levels had increased. The active (isolates from Guinea pigs skin scrapping) and dormant cells (isolates from keratin free media) were distinguished by Reverse Transcriptase-PCR. Collectively, qPCR is a successive and feasible method for the diagnosis for Microsporum and Trichophyton species.
Author Contributions
Academic Editor: Mohammed A Elmetwally, Professor of Theriogenogy
Checked for plagiarism: Yes
Review by: Single-blind
Copyright © 2023 Sohir Youssef, et al.
 This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Citation:
Introduction
Dermatophyte species are strongly related group of filamentous pathogenic fungi. They are keratinophilic and keratinolytic, and responsible for superficial cutaneous fungal infection of human and other animals, particularly cats and dogs, with a high risk of spread designated as dermatophytosis or ringworm1. Three genera make up the dermatophytes: Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton. Although the causative agents of dermatophytosis in cats and dogs are mainly related to genera Microsporum and Trichophyton, most severe infections are caused by a small number of species, both Microsporum canis and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Household animals (cats and dogs), serve as reservoirs of dermatophyte species and their infections are thought to be important zoonotic agents 2. Dermatophyte infects 25% of world population due to close proximity to pets either in rural or urban areas 3. Multifocal alopecia, scaling, circular skin lesions with fine, powdery scales, and hairs damaged at their base are the main symptoms of this infection. There is various diagnostic tools of dermatophytes involving conventional and molecular methods. The conventional identification of dermatophyte includes direct microscopy and culture as the gold-standard method. The fungal isolation is more accurate from skin scrapping with the back of sterile scalp than brush technique 4, 5. Reverse transcriptase PCR, one-step PCR, nested PCR, and real-time PCR have all been used in the molecular identification of dermatophytes 6. Although PCR has been used to identify Microsporum and Trichophyton, investigations on its usage with clinical samples from veterinary samples were few. Usually, these data employs for scientific research and have no validation for regular utilization in clinical work.
The development of a reference antifungal susceptibility testing technique may enable the clinician to choose the best course of treatment for illnesses brought on by dermatophytic fungus. The evaluation of in-vitro susceptibility testing has been complicated by a scarcity of trustworthy in-vitro methods for testing antifungal drugs against dermatophytes. In comparison to the microdilution assay, the agar disc diffusion assay for dermatophytes is quick, simple, affordable, and does not need special equipment 7. Itraconazole, terbinafine, and griseofulvin are three antifungals frequently used in systemic therapy of dermatophytosis in felines and canines 8. Drug resistance is currently one of the biggest obstacles for treating skin fungal infections, particularly in tropical and subtropical illnesses brought on by dermatophytes 9. In order to choose an effective antifungal medication against the clinical isolates and to optimise the therapy, in vitro antifungal susceptibility testing may be useful 10.
Animals can be experimentally infected to research the pathophysiology of fungal infections, the effectiveness of antifungal therapeutics as preventative measures, and the immunology of dermatophytosis 11. The use of guinea pigs as animal models for dermatophytosis is based on the predisposition of this species to skin fungal infections with clinical features comparable to those seen in humans12.
Although, in many countries, the prevalence of dermatophytes in cats and dogs is studied 13, there are extremely few reports on dermatophytes in cats and dogs and their antifungal susceptibility in the study area were noted. Furthermore, the pathogenesis study of dermatophytes (M. canis and T. mentagrophytes) through experimental infection in guinea pigs has not yet carried out in Egypt. Therefore, the goal of the current study was determination of the prevalence of dermatophyte and their antifungal susceptibility in domesticated animals, including cats and dogs that are thought to be the most potent carriers of the disease in Egypt. Also, the purpose of this study was to analyze the effects of dermatophyte infection on guinea pigs by studying clinical signs, fungal culture, leukogram, and reverse transcriptase PCR for clinical samples.
Materials and Methods
Ethical approval
The Faculty of Veterinary Medicine's Ethics Committee gave its approval to the collection method, Mansoura University (Mansoura, Egypt) and completed in accordance with the necessary biosecurity rules, and all laws and recommendations were followed when performing animal research of the "Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals".
Study population
The samples were collected by veterinarians from various private and public veterinary clinics based on Oxford Academic technique to improve molecular diagnosis of dermatophytosis in pet animals. A total of 200 animals (130 cats and 70 dogs) were tested in this research. Veterinarians documented and sequentially categorized as suspected cases of dermatophytosis animals with skin lesions such as alopecia and numerous circular lesions (figure 2. A). No antifungal medication was administered to any of the sampled animals either before or during the sampling. The current investigation was conducted between June 2019 and July 2020 in Dakahlia Government, Egypt.
Sampling
The clipped hair and skin scrap samples of each animal with probable dermatophytosis were collected from the lesions with both methods; scrubbing and brushing as previously described. In brief, scrubbing method was performed by first cleaning the area with alcohol 70% then scrubbing the skin surface at the edges of the area with the back of sterile scalpel. Brushing method was done to obtain hair samples by using a sterile brush cut after brushing the animal body for 5 min from head to tail. The animal body was brush for 3 min from head to tail. The samples were collected in a sterile tube contains peptone water broth (BioLab, Hungary), and transported to the laboratory within 24 h for further examination.
Dermatophytes culture
Skin scraping, clipped hair, and brush samples were inoculated into Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) (Biolab) and potato dextrose agar (PDA) (Difco), both of which were supplemented with Modified Dermato Supplement (HiMedia, India). The plates were incubated at 25°C for at least 14 days, and fungal growth was monitored daily. After incubation, lactophenol cotton blue was used to identify each isolate macroscopically and microscopically in terms of hyphae, macroconidia, and microconidia 14. The pure culture was stored on PDA for further analysis.
Antifungal susceptibility tests
According to the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute, agar disc diffusion and broth microdilution assays were used to assess the antifungal susceptibility of dermatophyte isolates 15. Briefly, the inoculum suspensions were made using CLSI recommendations from cultures that were cultivated on PDA without the use of antimicrobial agents and were 7 days old 16. Then, the suspensions were diluted to 1x106 CFU/ml and adjusted using a spectrophotometer (IMPLEN) to optical densities ranging from 0.29 to 0.34 at 635 nm for use in both the broth and agar techniques 17. Agar diffusion test was performed onto Muller Hinton agar plates (Oxoid) and using the following antifungal agents (Oxoid): Itraconazole (10 µg), fluconazole (10-25 µg, Sedico), nystatin (100U), griseofulvin (10 µg, Kahira P harma), amphotericin B (100U), terbinafine (10-25 µg, Global Napi). The plates were observed daily for 5-7 days 18. Microdilution test was applied using the following antifungal drugs: Itraconazole (Global Napi), fluconazole (Sedico), nystatin (Epico), griseofulvin (Kahira Pharma), terbinafine (Global Napi), and acetic acid (SDFCL). In brief, in a 96-well microtitre plate, stock solutions were used to create two-fold drug serial dilutions that were then produced in peptone broth (Oxoid). M. canis and T. mentagrophyte were introduced to each well at a concentration of 1x106each. The plates were incubated for 7 days at 25°C. The results were read by ELISA reader (BioTek, USA) at 560 nm before (0 day) and after incubation (7 days) for comparison 19.
Experimental design
Animals
Eighteen adult guinea pigs from local animal house weighing 350-450 gm were selected for this study. The housing was completed in the faculty of veterinary medicine at Mansoura University in Egypt's department of bacteriology, mycology, and immunology. Water and food were freely available to all animals. The feed pellets contained no antibacterial medications. They were housed in cages with regular air conditioning and a 14-hour light cycle.
Inoculum preparation
M. canis and T. mentagrophytes isolates obtained from local cases of canine and feline dermatophytosis as described above were used as challenge strains. The isolates were cultivated in PDA and incubated at 25°C for 14th days. The fungal suspensions with hyphal fragments were washed twice with phosphate buffered saline (PBS). The spores count was adjusted to 1x106 CFU/ml by measuring the optical density (OD) of suspensions using spectrophotometer (IMPLEN) at 635 nm.
Animals infection
The animals (n=18) were randomly divided (six in each group) into three main groups: Negative control group that did not get the fungus suspension vaccination (G1), infected group with M. canis (G2) and infected group with T. mentagrophytes (G3). A 1 ml of 1x106 CFU/ml suspensions (approximately 0.3 nm) was applied on the bare area with a sterile cotton swab, a single time. Skin scrapings, hair cultures, and clinical examination of infected skin lesions on the 7th and 14th day served as evidence that each animal had a fungal infection 20. On the 14th day, blood samples were collected for total and differential leukocyte count using veterinary automated CBC machine (ABAXIS) 4
Preparation and isolation of RNA
The total RNA was extracted from 1) culture of M. canis and T. mentagrophytes (n=3, each) grown on keratin free potato dextrose broth and 2) skin scrap samples (n=12, each) collected from experimental animals 3) control strain M. canis (AUMC 14454) and T. mentagrophytes (AUMC 14492) using combination of crude and RNA extraction kit 21. In brief, the samples were centrifuged at 1600g for 10 minutes after being rinsed twice with 10 ml of neutral, sterile, ice-cold PBS. Then, a small piece of the pellet (1-20 µg) was transferred to a sterile porcelain mortar and ground to powder with liquid nitrogen. After that, the resulting powder was suspended in a solution made up of 1 mL of Trizol reagent and 1 mL of lysis buffer (vivantis, Malaysia) with homogenizer for 2 min. Subsequently the homogenate was centrifuged using ultra-centrifuge (Sigma, D-37520 osterode am Harz) at 13,000 g/10min. The supernatant was then centrifuged at 13,000 g/20s with 70% ethanol. Following the manufacturer's instructions, the pelleted RNA was then added to the column of the RNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN,Germany) and ultra-centrifuged at 13,000 g/20s. The pellet was then ultracentrifuged at 13,000 g/20s after being washed with 700 µl of first wash buffer (RW1). The pellet was then ultracentrifuged twice and washed with 500 µl of second wash (RBE) (firstly for 20s and secondly for 2min). Finally, 50 µl of Elution H2O was used to elute the extracted RNA for 20 seconds. According to the MIQE recommendations, the concentration of total RNA was measured using a nanophotometer (IMPLEN) 22. RNA samples with A260/280 and A260/230 ratios were used for further analysis 23.
Reverse transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
RevertAid first strand cDNA synthesis kit (Thermo, US) was used to perform Reverse Transcriptase -PCR on total RNA as per the manufacturer's instructions and with random hexamer primers. The transcription reaction mixture contained (1µl random hexamer,2µg of total RNA, 4 µl 5x RNA PCR reaction buffer, 2µ of 10mM deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) mixture, 1µl of RiboLock RNase inhibitor (20U/µl), 1µl of RevertAid M-MuLV Reverse Transcriptase (200U/µl) and volume up to 20 µl with nuclease free water). The mixture was incubated in the DNA thermal cycler (Thermo scientific, ARKTIK) at 42°C for 60 minutes, followed by 5 minutes at 70°C.
In the DNA Thermal Cycler, cDNA was amplified in a total volume of 20 µl, which included 10 µl of 2 PCR Mastermix (Takara, Japan), 1 μL of individual primer responsible for the protein lysis F 5’- GGC TCT GAC CTG GAG AGT TG-3’ and R 5’- CGT TGT GAA CCT TGG AGG AT -3’ (Vivantis Technologies, Malaysia), 6 μL nuclease free water, and 1 μL cDNA template. The conditions for the PCR cycling step were as follows: a denaturation step at 95 °C for 1 min, then 40 cycles of incubation, each consisting of 95 °C for 30 sec, 60 °C for 30 sec, 72 °C for 30 sec, and final polymerization at 72 °C for 10 min.
Three percent agarose gel was used to separate the Reverse Transcriptase -PCR product (vivantis, Malaysia) incorporating 0.1-0.5 µg/ml ethidium bromide (vivantis, Malaysia) and photo-documented in Gel casting apparatus (Cleaver Scientific Ltd, UK).
Statistical analysis
The results' data analysis was carried out using an IBM compatible computer with SPSS software version 26.0. (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). As a result, frequency and percentage were used to express qualitative data. The geometric mean, MIC, and IC50 quantitative values were computed for the purpose of analysis. The p values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant 24.
Results
Prevalence of Microsporum and Tricophyton species in cats and dogs
Out of 200 samples from cats and dogs, 90 (45%) samples were positive for Microsporum (Figure 1. a1, a2 & a3) and Tricophyton (Figure 1.b1, b2 & b3) species by conventional mycological technique. Out of 130 samples from cats, M. canis (n=34/63; 53.9%) and T. mentagrophytes (n=29/63; 46%) were isolated from 63 cats (63/130, 48.5%) samples. Among the 70 samples from dogs, 27 (38.6%) samples were positive for M. canis (n=12/27; 44.4%) and T. mentagrophytes (n=15/27; 55.6%) as seen in (Table 1).
Figure 1.Microscopic examination of dermatophytes A) Macroconidia of Trichophyton Mentagrophytes (lactophenol cotton blue) detected from diseased animal (A1: 10x; A2: 40X; A3: 100X). B) Macroconidia of Microsporum canis (lactophenol cotton blue) detected from diseased animal (B1:10X; B2:40X; B3:100x).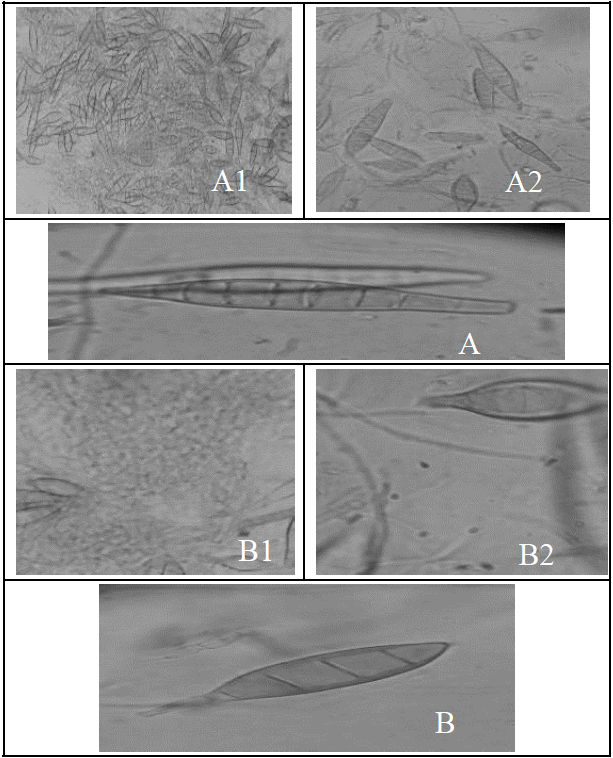
| Total examined samples | No of Trichophyton species | No.of Microsporum species | Total No of positive samples | ||
| Cats | 130 | 29(46%) | 34(53.9%) | 63(48.5%) | |
| Dogs | 70 | 15(55.6%) | 12 (44.4%) | 27(38.6%) | |
| Total | 200 | 44 (22% of the total and 48.8% of the positive) | 46 (23% of the total and 51% of the positive) | 90 (45%) |
Antifungal susceptibility test results
The antifungal susceptibility of 88 dermatophyte (M. canis n=44 and T. mentagrophytes n=44) strains to Itraconazole, fluconazole, nystatin, griseofulvin, amphotericin B, and terbinafine was examined by agar disk diffusion test result in (Table 2).
Table 2. Antifungal susceptibility of Microsporum species and Trichophyton species by agar disk diffusion method (n=88).| Species (No) | Antifungal agents | Potency | No. of samples (%) | Range of IZ (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | I | R | ||||
| Microsporum (44) | Itraconazole | 10 µg | 0 | 32(72.7%) | 12(27.3%) | 4-6 |
| Fluconazole | 10 µg | 0 | 0 | 44(100%) | 0-5 | |
| 25 µg | 0 | 3(6.8%) | 41(93.2%) | 16-18 | ||
| Nystatin | 100U | 30(68.2%) | 6(13.6%) | 8(18.2%) | 48-101 | |
| Griseofulvin | 10 µg | 33(75%) | 11(25%) | 0 | 70-107 | |
| Amphotericin B | 100U | 0 | 0 | 44(100%) | 5-8 | |
| Terbinafine | 10 µg | 30(68.1%) | 9(20.5%) | 5(11.4%) | 49.8-51.5 | |
| 25 µg | 31(70.5%) | 12(27.3%) | 1(2.2%) | 72-74 | ||
| Trichophyton (44) | Itraconazole | 10 µg | 12(27.3%) | 15(34.1%) | 17(38.6%) | 23-40 |
| Fluconazole | 10 µg | 0 | 0 | 44(100%) | 5-6 | |
| 25 µg | 0 | 1(2.3%) | 43(97.7%) | 15-16 | ||
| Nystatin | 100U | 25(56.8%) | 15(34.1%) | 4(9.1%) | 17-19 | |
| Griseofulvin | 10 µg | 27(61.4%) | 8(18.1%) | 9(20.5%) | 42-60 | |
| Amphotericin B | 100U | 0 | 4(9.1%) | 40(90.9%) | 10-11 | |
| Terbinafine | 10 µg | 20(45.5%) | 22(50%) | 2(4.5%) | 50-52 | |
| 25 µg | 24(54.5%) | 20(45.5%) | 0 | 74-83 | ||
Microsporum canis showed high susceptibility to griseofulvin (75%), followed by terbinafine 25µg (70.5%), nystatin (68.2%), and terbinafine 10µg (68.1%), while Trichophyton mentagrophytes revealed high sensitivity to griseofulvin(61.4%), followed by nystatin (56.8%), terbinafine 25µg (54.5%), terbinafine 10µg (45.5%), and Itraconazole (27.3%). On the other hands, no antifungal activity of fluconazole and amphotericin B was observed against dermatophytes. In particular, Itraconazole showed no sensitivity to all examined Microsporum species.
The MICs of fluconazole, nystatin, griseofulvin, terbinafine, and acetic acid for 10 dermatophyte isolates, including M. canis (n=5) and T. mentagrophytes (n=5), were evaluated using the broth microdilution assay. MIC range, MIC, IC50 range, IC50 and geometric mean MIC were computed (Table 3).
Table 3. Microsporum canis and Trichophyton mentagrophytes Minimal inhibitory concentration, IC 50 and geometric mean against different antifungal drugs with different concentration| Species (No) | Antifungal agents | MIC range | MIC (µg/ml) | IC 50 range | IC 50 (µg/ml) | GM range | GM |
| M. canis (5) | NY | 0.999-1.99 | 1.08 | 0.55-1.1 | 0.60 | 0.3-0.5 | 0.3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRE | 0.88-2 | 1.24 | 0.5-1.16 | 0.69 | 0.38-0.78 | 0.59 | |
| FLU | 1-1.49 | 1.3 | 0.59-0.8 | 0.72 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.6 | |
| ACETIC ACID | 1.02-1.6 | 1.05 | 0.58-0.9 | 0.58 | 0.3-0.5 | 0.4 | |
| TER | 0.9-1.05 | 0.98 | 0.5-0.58 | 0.54 | 0.49-0.68 | 0.59 | |
| T. mentagrophyte(5) | NY | 0.4-0.439 | 0.4199 | 0.2-0.24 | 0.23 | 0.02-0.12 | 0.12 |
| GRE | 0.75-6.667 | 4.6875 | 0.37-0.7 | 2.6 | 0.03-0.16 | 0.134 | |
| FLU | 0.37-0.749 | 0.587 | 0.2-0.41 | 0.33 | 0.03-0.14 | 0.13 | |
| ACETIC ACID | 0.246-0.4 | 0.28 | 0.13-0.2 | 0.16 | 0.026-0.1 | 0.1 | |
| TER | 0.22-0.328 | 0.295 | 0.1-0.18 | 0.16 | 0.02-0.14 | 0.14 |
In general, the information demonstrated that the most effective antifungal agent tested against dermatophytes was terbinafine and acetic acid. For M. canis strains, the lowest MIC was observed to terbinafine (MIC = 0.98 µg/ml; IC50 = 0.54 µg/ml) followed by acetic acid (MIC = 1.05 µg/ml; IC50 = 0.58 µg/ml), nystatin (MIC = 1.08 µg/ml; IC50 = 0.6 µg/ml), griseofulvin (MIC = 1.24 µg/ml; IC50 = 0.69 µg/ml), and fluconazole (MIC = 1.3 µg/ml; IC50 = 0.72µg/ml). While among T. mentagrophytes strains, the lowest MIC was detected to acetic acid (MIC = 0.28 µg/ml; IC50 = 0.16 µg/ml) followed by terbinafine (MIC = 0.295 µg/ml; IC50 = 0.16 µg/ml), nystatin (MIC = 0.4199 µg/ml; IC50 = 0.23 µg/ml), fluconazole (MIC = 0.587 µg/ml; IC50 = 0.33 µg/ml), and griseofulvin (MIC = 4.6875 µg/ml; IC50 = 2.6 µg/ml).The viability of M. canis strains was decreased after treatment with nystatin, and acetic acid, followed by fluconazole, terbinafine, and griseofulvin in the lowest concentration and reached 20-30%. For T. mentagrophytes, the lowest viability was detected to acetic acid followed by nystatin, and fluconazole ranges from 60-80%, while the highest viability (90-100%) to terbinafine and griseofulvin was observed (Figure 3).
Figure 3.The fungal viability (%) after antifungal treatment.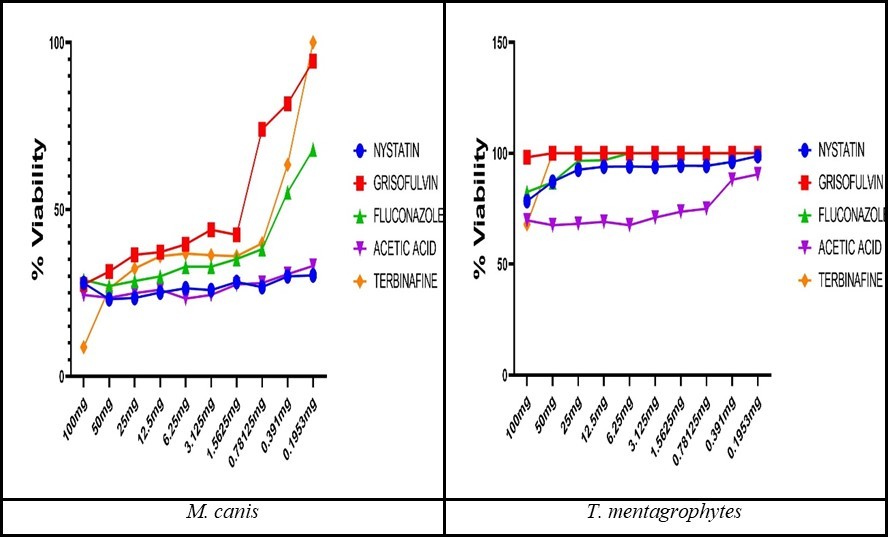
Experimental infection results
Clinical signs and culture after dermatophytes infection
All of the guinea pigs (G2 & G3) exposed to the fungus during the experimental infection with M. canis or T. mentagrophytes developed lesions (Figure 2).
Figure 2.Dermatophyte lesion on the skin of infected animals a) naturally infected cat b) experimentally infected guinea pig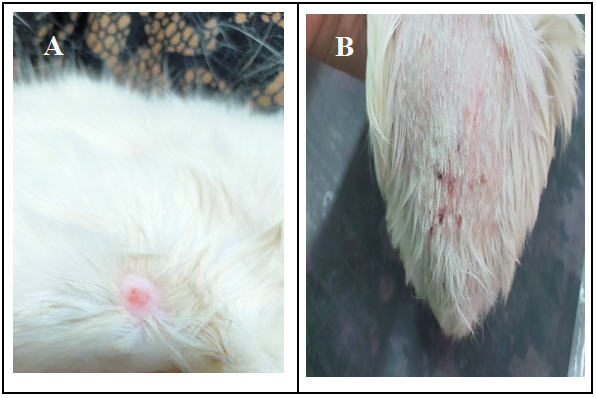
The first symptoms of infection appeared in all affected animals on the seventh day following inoculation and ranged from dandruff-like scalps to hair loss. Some animals showed pruritus with itching and scratching of the lesion. Around the 14th day, these alterations became more evident with the development of hair rarefaction and squamosis. The lesions gradually increased in diameter with the development of complete hair loss and crust formation between the 10th and 14th days. All infected animals' skin scrapings and hair from days 7 and 14 were used to re-isolate M. canis and T. mentagrophytes. All of the animals that had received the inoculation tested positive for mycological cultures (Figure 4).
Figure 4.Macroscopic appearance of M. Canis on potato dextrose in a falcon A) Bright yellow reverse pigment B) white, fluffy with areal mycelium surface; Macroscopic appearance of T. Mentagrophytes on Sabouraud dextrose agar plate C) colorless, yellow brown reverse pigment and D) white creamy granular surface.
Leukogram analysis
G1, Control group; G2, M. canis infected group; G3, T. mentagrophytes infected group; the results represent significant results (mean ± SD) (P > 0.002).
The total leukocytes count is significantly elevated in all infected groups (4-6x109/µl for G2 and 6-8X109/µl for G3) at 14 days post infection compared to G1 group (approximately 2X109/µl). The differential leukocytes count showed that lymphocyte and neutrophil were raised in comparison with monocyte. The neutrophil level was significantly elevated to 2-4.5 X109/µl in G2 and 5.4-6.3 x109/µl in G3 in comparison to G1 at 14th days post infection. The lymphocyte level was raised to 1.3-2.2 x109/µl in G2 and 0.9-1.2 x109/µl in G3 compared to G1. Also, the monocyte level was increased to 0.4-0.5 x109/µl in G2 and 0.2-0.8 x109/µl in G3 compared to G1. The result was tabulated below (Table 4).
Table 4. Total Leukocytes Count (TLC) of experimentally infected (M. canis or T. mentagrophytes) guinea pigs.| G1 | G2 | G3 | ||
| TLC | mean | 2.21 x109/µl±0.06 | 5.45 x109/µl±0.38 | 7.05 x109/µl±0.75 |
| range | 1.9-2.4x109/µl | 4-6x109/µl | 6-8x109/µl | |
| STD | 0.14 | 0.9 | 0.75 | |
| Neutrophil | mean | 1.1 x109/µl±0.07 | 3x109/µl±0.35 | 5.74 x109/µl±0.15 |
| range | 0.95-1.3 x109/µl | 2-4.5 x109/µl | 5.4-6.3 x109/µl | |
| STD | 0.17 | 0.86 | 0.36 | |
| Lymphocyte | mean | 0.71 x109/µl±0.01 | 1.95 x109/µl±0.15 | 0.995 x109/µl±0.05 |
| range | 0.7 x109/µl | 1.3-2.2 x109/µl | 0.9-1.2 x109/µl | |
| STD | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.13 | |
| Monocyte | mean | 0.08 x109/µl±0.03 | 0.47 x109/µl±0.02 | 0.445 x109/µl±0.11 |
| range | 0.02-0.2 x109/µl | 0.4-0.5 x109/µl | 0.2-0.8 x109/µl | |
| STD | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.27 |
Molecular analysis
Gel electrophoresis of the cDNDs of the dermatophyte (M. canis and T. mentagrophytes from skin scrap samples (n=6, each) obtained from experimentally infected guinea pigs revealed characteristic banding pattern with single protease targeted cDNA band in (Figure 5).
Figure 5.The Reverse Transcriptase -PCR amplification of dermatophytes gene (approximately 98 bp). Lane M: 50 bp ladder; lane 1: control positive Trichophyton mentagrophytes (Robin) Blanchard AUMC 14492 (C+); lane 2: control negative (C-); lane 3-5: Microsporum canis from experimentalyl infected Guinea pigs (M1, M2, M3); lane 6: M. Canis from culture (M.C); lane 7-9: T. Mentagrophytes from experimentally infected G. Pigs (T1, T2, T3); lane 10: T. Mentagrophytes from plate (T.M).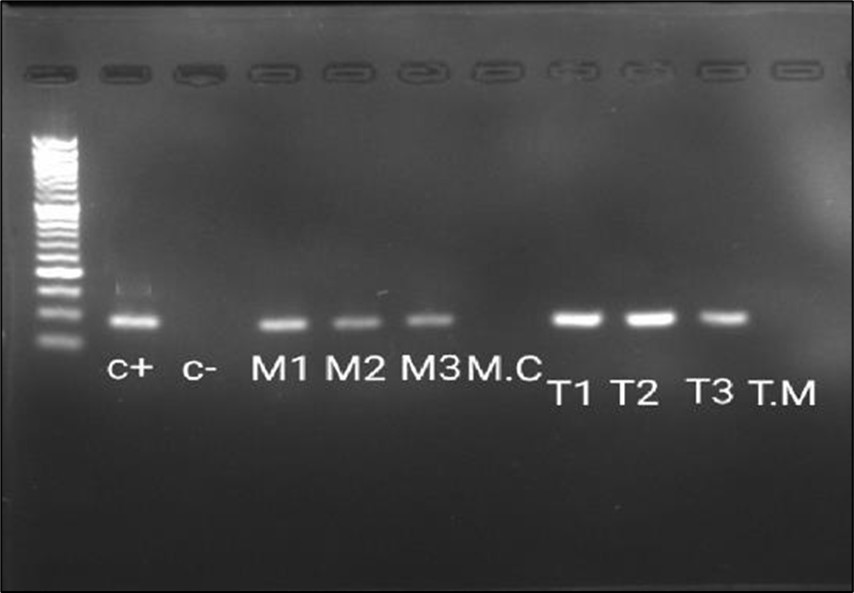
Discussion
Dermatophyte is one of the most widely spread diseases in the world particularly countries with poor sanitation and dense populations. Though it is not a fatal disease but it is rapidly spread and causes yearly huge economic losses in antifungal treatment 25. The fact that this disease is transmitted from animals to man and vice versa makes its proper diagnosis and control of great importance to help eradicate the disease 18. Especially that most cases goes miss diagnosed or not reported in Egypt as most owners do not seek veterinary service in skin diseases 26. Cats and dogs are regarded as one of the principal carriers of disease in a number of European nations 27. This study looked into the frequency of dermatophytes in Egyptian cats and dogs with dermatophytosis. In this study, standard mycological testing revealed that 90 (45 %) of the 200 samples analyzed contained fungal components. The prevalence of infections is typically more than 20% in cats, but it is between 4% and 20% in dogs, according to epidemiological studies on cats and dogs with probable dermatophytosis lesions 28–30. In this study, in particular, dermatophytes were identified from 48.5% of the cats and 38.6% of the dogs. In Spain and Egypt, previous studies revealed a prevalence that was two times higher in feline than in canines 26, 31, 32 detected the isolation rates of dermatophyte species (19.3%) from cats (20.1%) and dogs (18.7%). In a recent study performed on 10,678 and 15,684 cats and dogs samples only 23% were found positive for dermatophytes 33. In fact, our findings indicated that dermatophytosis can be prevalent feline and canine illnesses in Dakahlia Government, Egypt. Therefore, the higher isolation rate of dermatophytes among cats and dogs in the present study may be alarming in these areas of Egypt.
Numerous investigations have proven that systemic and topical antifungal treatments for dermatophytosis are ineffective 34, therefore, it is crucial to assess and standardize in-vitro assays that are straightforward and repeatable to ascertain the antifungal effectiveness of various medications against dermatophytes. Antifungal agent in-vitro activity studies are intermittent and primarily focus on filamentous fungi 35. The creation of a standardized disc diffusion agar-based assay is needed because it is highly straightforward, simple to use, easy to perform, and affordable, making it suited for use in routine testing. In this study, agar disc diffusion antifungal susceptibility tests were used to determine how susceptible 88 isolates of dermatophytes were to six commonly used antifungal medications (Itraconazole, fluconazole, nystatin, griseofulvin, amphotericin B, and terbinafine) for the treatment of dermatophytosis. Relative to the tested agents, griseofulvin, nystatin, and high concentration of terbinafine (25 µg) exhibited the best antifungal efficacy against those dermatophytes. On the other hands, no antifungal activity of fluconazole and amphotericin B was observed against dermatophytes. Also, Itraconazole showed no susceptibility to all examined Microsporum species. Our data concurred with previous study indicating the high susceptibility of examined dermatophytes to griseofulvin (46.4%) and high resistance to fluconazole (94.5%) 18 from clinical samples in Egypt. The research showed that fluconazole was the least potent antifungal agent 36. Another study found that dermtophyte strains showed higher susceptibility to terbinafine than griseofulvin, while Itraconazole and fluconazole had no effect on T. mentagrophytes24. In contrast, Fowora et al.37 detected the high sensitivity of T. mentagrophytes to Itraconazole, whereas griseofulvin had no effect in Nigeria. The development of resistance to fluconazole and Itraconazole, which were previously more effective on dermatophytes, may be due to their commonly and safely use on the contrary of other azole compounds 24.
According to these results of broth microdilution studies, the most effective drugs against M. canis and T. mentagrophytes were terbinafine and acetic acid, respectively, whereas the least effective drugs were fluconazole and griseofulvin, respectively. The antifungal efficiency of fluconazole was previously detected using microdilutiion test 38. Acetic acid is a commonly used house hold remedy (water vinegar mixture) for the fastest method of Dermatophyte treatment, particularly in cats and dogs. The lowest MIC values for ketoconazole, itraconazole, and amphotericin-B against M. canis, T. mentagrophytes, and M. gypseum isolated from cats and dogs, respectively, were found by Debnath et al. 39 in India. Fluconazole had the highest MIC activity (0-24 µg/ml), whereas itraconazole had the lowest MIC activity (0.03-0.5 µg/ml) against human dermatophyte isolates 40. The previous study showed low MIC of griseofulvin (2-4 μg/ml) and high efficacy of terbinafine (0.06-0.5 μg/ml) against dermatophytes isolates involving M. canis and T. mentagrophyte 41. Bossche 42 reported higher MIC result with IC50 of griseofulvin (0.5 µg/l) against M. canis. Nystatin is less effective towards dermatophytosis that leads to the unpopularity of this antifungal agent to local veterinarians. Zaman and Gupta 24 reported the following MIC values for griseofulvin (1 μg/ml) and terbinafine (0.004 μg/ml) against T. mentagrophytes. Recently, a study on T. mentagrophytes showed high antifungal activity of nystatin and griseofulvin in Nigeria 37. Our research demonstrates that in-vitro antifungal susceptibility testing is essential for the routine clinical laboratory assessment of dermatophyte susceptibility to antifungal drugs. It enables comparisons between various antifungal medications and can aid in improving the dermatophytosis treatment plan.
Most of Microsporum and Trichophyton species are saprophytic and found naturally in the environment and not necessary active or capable of inducing disease. Dermatophytes, which infect keratinized tissue in both people and animals, cause dermatophytosis, a superficial fungal infection. Dermatophytosis lesions display an inflammatory response that is brought on by the host's natural immunological response to get rid of the invading fungi 20. Due of its high receptivity, ease of handling, and reproducibility, and the guinea pig has been utilized as a model extensively. In our investigation, guinea pigs that were experimentally infected with either M. canis or T. mentagrophytes developed a variety of lesions that started to appear on day seven after infection and became more noticeable around day 14 in all exposed animals. There were several clinical signs among model animals infected by a dermatophyte ranging from erythema and red papules to typical signs of T. mentagrophytes of thick scales, and crust that reach its peak at day 14th day post infection 20, 43. These results support the observations made by 44, who used guinea pigs to test the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a Microsporum canis metalloprotease subunit vaccine. They noted slight but characteristic dermatophytosis-like symptoms on the seventh day after inoculation. Additionally, 87.5 % of the G. pigs exhibited the first symptoms around the fifth day following M. canis inoculation, as shown by the presence of moderate edema, erythema, and mild shedding 12.
The leukogram is unspecific indicative for the infection. In the current study, the leukocytes mass finding of the infected G. pigs at 14 days post infection revealed significant leukocytosis, particularly lymphocytosis which may be due to Th1 response towards the proteases secreted by the fungi 4. In the present study, the infected groups showed a significant neutrophilic leukocytosis as the stress and the severity of the inflammation in response to infection causes attraction of neutrophils to the site of fungal infections 45. Additionally, the monocytosis profile observed in infected G. pigs provides evidence that M. canis and T. mentagrophytes consistently stimulated monocytes and polymorphonuclear neutrophils, two types of leucocytes 46. DNA identification tools are expensive, not always available and not accurate as it may not be active or the sole cause of the disease. The need to find a new tool to diagnose active fungi that are capable of disease production and can be used on both Microsporum and Trichophyton species becomes a necessity. Keratin lytic producing genes are encoded within the fungal genome and only expressed in the presence of keratin (skin, nails, and hair keratin rich parts) as a nitrogen source of energy. Although there are numerous published studies on the use of Reverse Transcriptase -PCR on specimens from experimentally infected G. pigs, there are few published studies on the identification of Microsporum and Trichophyton spp. using PCR 47. The current work detected the presence of gene responsible for the protein lysis in all examined samples using Reverse Transcriptase -PCR. The use of Reverse Transcriptase -PCR contributed in the identification of dermatophytes (Microsporum and Trichophyton species) and detection of their most virulence keratinase genes were recently stated 48–50. The infectivity of fungi is associated with its ability to produce keratinase enzyme 51.
Conclusion
The current study shed light on the prevalence of dermatophytes in cats and dogs in various regions of Egypt, which may act as human-to-human carriers in their hair or skin. M. canis and T. mentagrophytes were the two dermatophytes that were most frequently isolated from sick cats and dogs. These pets play important roles in the prevalence and dissemination of dermatophytosis in both animals and people. The current study exhibited MIC values of several antifungal drugs and offered helpful information on the antifungal susceptibility patterns of dermatophytes. Regular monitoring of antifungal susceptibility patterns in affected animals should be done in order to assist the doctor in starting quick and suitable antifungal medication. This paper reports the first experimental study of dermatophytes in guinea pigs in Egypt which will be useful for exploring the pathogenesis of dermatophytosis. Determining in detail which virulence factors are in charge of dermatophyte pathogenesis is the next hurdle.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the colleagues of Bacteriology, Mycology, and Immunology department, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Mansoura University for their assistance.
References
- 1.Osman M, Kasir D, Rafei R. (2022) Trends in the epidemiology of dermatophytosis in the Middle East and North Africa region. , Int J Dermatol 61, 935-968.
- 2.Gnat S, Łagowski D, Nowakiewicz A. (2021) A global view on fungal infections in humans and animals: infections caused by dimorphic fungi and dermatophytoses. , J Appl Microbiol 131, 2688-2704.
- 3.Mahela D V, DRD Mehta, DBC Ghiya. (2019) The Study of Magnitude of Dermatophytes and Its Correlation with Socio-Economic Status, Inhabitant, Age, Sex, and Occupation at North West Rajasthan. , East African Scholars J Med Sci 2-3.
- 4.Moriello K A, Coyner K, Paterson S. (2017) Diagnosis and treatment of dermatophytosis in dogs and cats. , Vet Dermatol 28, 266-68.
- 5.Moursi S. (2018) Epidemiological Studies on Dermatophytosis in Human in Hail Region of Saudi Arabia. , IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) 15(2), 80-84.
- 6.Arastehfar A, Wickes B L, Ilkit M. (2019) Identification of Mycoses in Developing Countries. , J Fungi (Basel) 5(4), 90.
- 7.Matheus Heita Namidi.Tejashree Ananthnaraja, Badveti Satyasai (2021). Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Dermatophytes by ABDD and E-Test, a Comparative Study. , Open J Med Microbiol 11(3).
- 8.Moriello Karen. (2019) Dermatophytosis in cats and dogs: a practical guide to diagnosis and treatment. In Pract 41(4), 138-147.
- 9.Gna Sebastian, Łagowski D, Nowakiewicz A. (2020) Major challenges and perspectives in the diagnostics and treatment of dermatophyte infections. , J Appl Microbiol 129(2).
- 10.de Sousa ESO, ACA Cortez, M de Souza Carvalho. (2020) Factors influencing susceptibility testing of antifungal drugs: a critical review of document M27-A4 from the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). , Braz J Microbiol 51(4), 1791-1800.
- 11.aahs Al-janabi.Al-khikani fho (2021). Prophylaxis and Therapeutic Ability of Inactivated Dermatophytic Vaccine Against Dermatophytosis in the Rabbits as an Animal Model. , Turk J Pharm Sci 18, 326-331.
- 12.Song X, Wei Y-X, Lai K-M. (2018) In vivo antifungal activity of dipyrithione against Trichophyton rubrum on guinea pig dermatophytosis models. , Biomed Pharmacother 108, 558-564.
- 13.Moosavi A, Ghazvini R D, Ahmadikia K. (2019) The frequency of fungi isolated from the skin and hair of asymptomatic cats in rural area of Meshkin-shahr-Iran. , J Mycol Médicale 29, 14-18.
- 14.Frías-De-León M G, Martínez-Herrera E, Atoche-Diéguez C E. (2020) Molecular identification of isolates of the Trichophyton mentagrophytes complex. , Int J Med Sci 17, 45-52.
- 15.Reem Mostafa Hassan. () Dalia Kadry Ismail, Yasmine Samy Elkholy (2017). Comparison of E Test and Disc Diffusion Methods for Susceptibility Testing of Filamentous Fungi; Experience of a Routine Lab. Arch Clin Infect Dis.
- 16.Jorgensen J H, Hindler J F. (2007) New consensus guidelines from the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute for antimicrobial susceptibility testing of infrequently isolated or fastidious bacteria. , Clin Infect Dis 44(2), 280-286.
- 17.Chakravarthi G, Reddy A, Ramaiah M. (2017) . , Assessment of Biological Activity and Comparison of UPLC and RP-HPLC Chromatographic Profiles of Clausena excavata Burm.F. Pharmacogn J 9, 185-191.
- 18.MFM Shalaby, El-din A N, El-Hamd M A. (2016) Isolation, Identification, and In Vitro Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Dermatophytes from Clinical Samples at Sohag University Hospital in Egypt. , Electron Physician 8, 2557-2567.
- 19.Kakande T, Batunge Y, Eilu E. Kampala International University Teaching Hospital, Uganda. Dermatol Res Pract (2019) Prevalence of Dermatophytosis and Antifungal Activity of Ethanolic Crude Leaf Extract of Tetradenia riparia against Dermatophytes Isolated from Patients Attending.
- 20.Shimamura T, Kubota N, Shibuya K. (2012) Animal Model of Dermatophytosis. , J Biomed Biotechnol 2012-125384.
- 21.Cortés-Maldonado L, Marcial-Quino J, Gómez-Manzo S. (2020) A method for the extraction of high quality fungal RNA suitable for RNA-seq. , J Microbiol Methods 170, 105855.
- 22.Bustin S A, Benes V, Garson J A. (2009) The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. , Clin Chem 55, 611-622.
- 23.Pandey S, Alam A, Chakraborty D. (2019) An Improved Protocol for Genomic DNA Isolation from Bryophyte Species. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect. , B Biol Sci 89, 823-831.
- 24.Singh J, Zaman M, Gupta A K. (2007) Evaluation of microdilution and disk diffusion methods for antifungal susceptibility testing of dermatophytes. , Med Mycol 45, 595-602.
- 26.Waly N, Kamel R, Ahmed L. (2017) Prevalence of dermatophytosis in dogs and cats in Egypt. BSAVA Congr. Proc. 2017. British Small Animal Veterinary Association 457-457.
- 27.Moraru R, Chermette R, Guillot J. (2019) Superficial Mycoses in Dogs and Cats. In:. Singh K, Srivastava N, editors Recent Trends Hum. Anim. Mycol 27-45.
- 28.RSN Brilhante, CSP Cavalcante, Soares-Junior F A. (2003) High rate of Microsporum canis feline and canine dermatophytoses in Northeast Brazil: epidemiological and diagnostic features. , Mycopathologia 156, 303-308.
- 29.Cafarchia C, Romito D, Sasanelli M. (2004) The epidemiology of canine and feline dermatophytoses in southern Italy. , Mycoses 47, 508-513.
- 30.Mancianti F, Nardoni S, Cecchi S. (2003) Dermatophytes isolated from symptomatic dogs and cats in Tuscany, Italy during a 15-year-period. , Mycopathologia 156, 13-18.
- 31.Cabañes F J, Abarca M L, Bragulat M R. (1997) Dermatophytes isolated from domestic animals in. , Barcelona, Spain. Mycopathologia 137, 107-113.
- 32.Seker E, Dogan N. (2011) Isolation of dermatophytes from dogs and cats with suspected dermatophytosis in Western Turkey. , Prev Vet Med 98, 46-51.
- 33.Moretti A, Agnetti F, Mancianti F. (2013) Dermatophytosis in animals: epidemiological, clinical and zoonotic aspects. , G Ital Dermatol Venereol 148, 563-572.
- 34.Galuppi R, Gambarara A, Bonoli C. (2010) Antimycotic effectiveness against dermatophytes: comparison of two in vitro tests. , Vet Res Commun 34, 1-57.
- 35.Sharma C.Chowdhary A (2017). Molecular bases of antifungal resistance in filamentous fungi. , Int J Antimicrob Agents 50, 607-616.
- 36.Magagnin C M, CDO Stopiglia, Vieira F J, Heidrich D. (2011) Antifungal susceptibility of dermatophytes isolated from patients with chronic renal failure. , An Bras Dermatol 86, 694-701.
- 37.Fowora M A, Onyeaghasiri F U, ALO Olanlege. (2021) . In Vitro Susceptibility of Dermatophytes to Anti-Fungal Drugs and Aqueous Acacia nilotica Leaf Extract in Lagos , Nigeria, J Biomed Sci Eng 14, 74-82.
- 38.Rochette F, Engelen M, Vanden Bossche H. (2003) Antifungal agents of use in animal health – practical applications. , J Vet Pharmacol Ther 26, 31-53.
- 39.Debnath C, Mitra T, Kumar A. (2016) Detection of dermatophytes in healthy companion dogs and cats in eastern India. , Iran J Vet Res 17.
- 40.Aktas A E, Yigit N, Aktas A. (2014) Investigation of In Vitro Activity of Five Antifungal Drugs against Dermatophytes Species Isolated from Clinical Samples Using the E-Test Method. , Eurasian J Med 46, 26-31.
- 41.Samia A Girgis, El-fakkar Nehal M Zu, Badr Hala. (2006) genotypic identification and antifungal susceptibility pattern of dermatophytes isolated from clinical speciments of dermatophytosis in egyptian patients. , Egyptian dermatology 2(2), 1-23.
- 42.Bossche Vanden. (2017) Antifungal agents of use in animal health – chemical, biochemical and pharmacological aspects. , J Vet Pharmacol Ther 26(1), 5-29.
- 43.Fontenelle R O, Morais SM de, EHS Brito, Nascimento NRF do, Valença Júnior JT. (2014) Experimental dermatophytosis on the outer ear of guinea pigs: a model that mimics natural infection. , RUVRV 12(1).
- 44.Vermout S M, Brouta F D, Descamps F F. (2004) Evaluation of immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a Microsporum canis metalloprotease subunit vaccine in guinea pigs. , FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 40, 75-80.
- 46.Gihan M Mohamed, MKheiralla Zeinab, AbdelNasser Moustafa. (2016) . Effect of Dermatophytes on Neutrophils and Monocytes Chemotaxis. MOJ Immunol.3(3) 00089.
- 47.Ungo-kore H Y, Ehinmidu J O, Onaolapo J A. (2021) Molecular Characterisation and Phylogenetic Analysis of Dermatophytic Fungi Isolated from Tinea Capitis in Northwest Nigeria Using Sequence of the 28S rRNA. , Microbiol Res 12, 646-655.
- 48.Achterman R R, White T C. (2012) Dermatophyte virulence factors: identifying and analyzing genes that may contribute to chronic or acute skin infections. , Int J Microbiol 2012, 358305.
- 49.Baeza L C, Bailão A M, Borges C L. (2007) cDNA representational difference analysis used in the identification of genes expressed by Trichophyton rubrum during contact with keratin. , Microbes Infect 9, 1415-1421.