Possibility to Influence Treatment of Open Tibial Fracture by Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Abstract
Modern medicine gives treatment options even in cases, where this has not been possible in the past. We want to present how negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) helps in limb salvage. The case report brings our insight and experience on how to be successful with NPWT.
We present a high-energy injury with an open tibial fracture IIIB according to Gustillo-Anderson classification 11. NPWT is an excellent option to treat extensive soft tissue injury. NPWT is also beneficial in the application of the dermoepidermal graft as we have found. We can confirm that this therapy contributed to a faster healing of soft tissues compared to classical wound healing.
Author Contributions
Academic Editor: Inarei José Pnarei Júnior, Faveni-Faculty New Immigrant Sale, Brazil.
Checked for plagiarism: Yes
Review by: Single-blind
Copyright © 2019 MUDr. Miroslav Budoš, et al.
 This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Citation:
Introduction
Medicine, as well as other disciplines over the past few years, has had a progressive rise in the field of healing. Today's possibilities push the treatment forward and we are able to heal effectively what we could not be able heal in the past. We want to present two case reports with serious injury of tibia and soft tissue. These are two high-energy limb trauma with an open tibial fracture. The mechanism of injury in both cases is the passing of the limb by the bus wheel. Both patients were treated in a specialized clinic and the procedure of diagnostic and osteosynthesis was standard trauma protocol. An important part for the treatment of soft tissues was the vacum therapy called negative pressure wound therapy or vacum assisted closure therapy (V.A.C.). In both cases there was no injury to marginal vessels and nerves. Ischemia on the periphery or missing pulse was not detected. Mess score classification was used to determinate surgery strategy. 1
NPWT is a modern and successful treatment of soft tissues. The principle of therapy is a closed system of controlled negative pressure environment wound. The vacuum system drains the exudate into the special container. Eliminates infection or reduced bacterial colonization in the wound. Vacuum stimulates granulation by local hyperemia and also promotes neovascularization. Secretion removal further contributes to reducing soft tissue swelling around the wound and reducing limb edema. 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
Biological acceptability has been demonstrated in animal models where vacuum therapy leads to decreased swelling, increased tissue perfusion and increased granulation tissue. 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
An open fracture and high-energy trauma in relation to the time of treatment present a risk of slow bone healing. NPWT heals faster soft tissue and gives the possibility of better bone healing.
Materials and Methods
We present two case reports with serious injury of tibia and soft tissue. It is high-energy limb trauma with an open tibial fracture. Both patients were treated at a specialized traumatic clinic with standard traumatic guidance. Urgent initial laboratory examination, diagnostics (X-ray, CT, AGCT) and osteosynthesis up to 6 hours with soft tissue treatment.
An important part for the treatment of soft tissues was the negative pressure wound therapy. We cooperate with Hartmann company and use Vivano device.
The method that influenced treatment in these cases was vacuum therapy. The principle is a closed system of controlled negative pressure environment wound or defect. The wound is primarily cleaned and free of necrotic parts and then covered with a special polyurethane foam. Then the wound with foam is covered with a special thin foil. A closed environment is created. In the middle of the foil is a hole with a special port with tubing, which is connected to the device. The device maintains a stable vacuum 125 mmHg and removes secretions from the wound. The vacuum is maintained continuously throughout the treatment period.
The vacuum system drains the exudate into the special container. Eliminates infection or reduced bacterial colonization in the wound. Vacuum stimulates granulation by local hyperemia and also promotes neovascularization. Secretion removal further contributes to reducing soft tissue swelling around the wound and reducing limb edema. 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
In our case we are using vNPWT for open fractures of tibia type G-A IIIB. Parts of the skin cover were destroyed by injury. Parts were loss of skin and subcutaneous defects or necrotic decollemetal parts. In this case we used a synthetic skin cover at the beginning (Synkryt), and then vacuum therapy.
We hade used dermoepidermal graft as a method of definitive closure of skin defects. This method is simple and has less nutritional requirements than a full thickness graft.
Graft is in thickness 0.3-0.4 mm and contains dermis and epidermis structures. Removal graft performed using an electrodermatome in the required size.
Standard metods to acute treatment in the department of emergency admission is debrits of the limb, desinfection, antiseptic dressing, temporary fixation, diagnostics (X-ray, CT, angiography, angio CT), initial ATB therapy, urgent preoperative preparation, transport to the operation hall.
Our Acute Surgery methods are complete limb debritman, excision of necrotic parts of skin, subcutis, removal of other microscopic impurities. Than stabilization of the tibia OS by external fixation. Reconstruction of soft structures, muscles, fascias, subcutis and skin. Application of Synthetic Skin Cover /Synkryt / or NPWT immediately. Limb wound dressing for vacuum therapy is every 4-5 days.
Case No.1
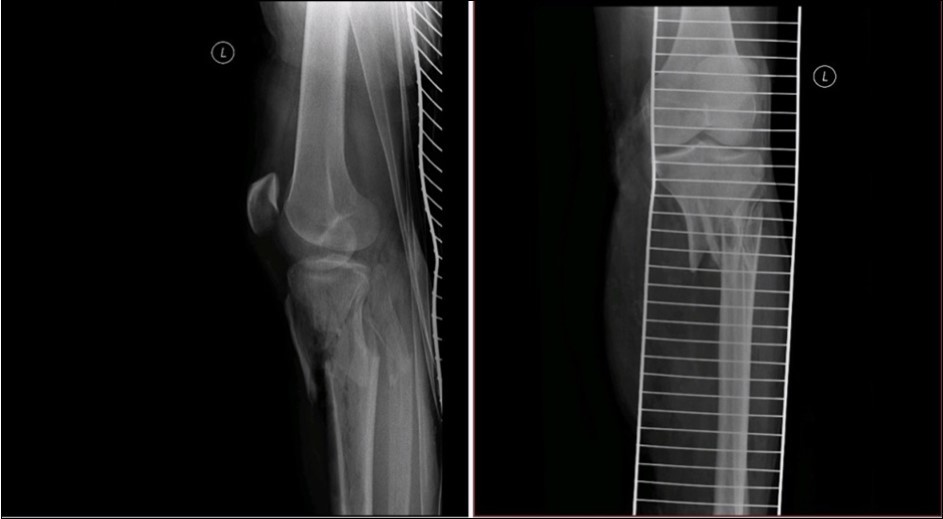
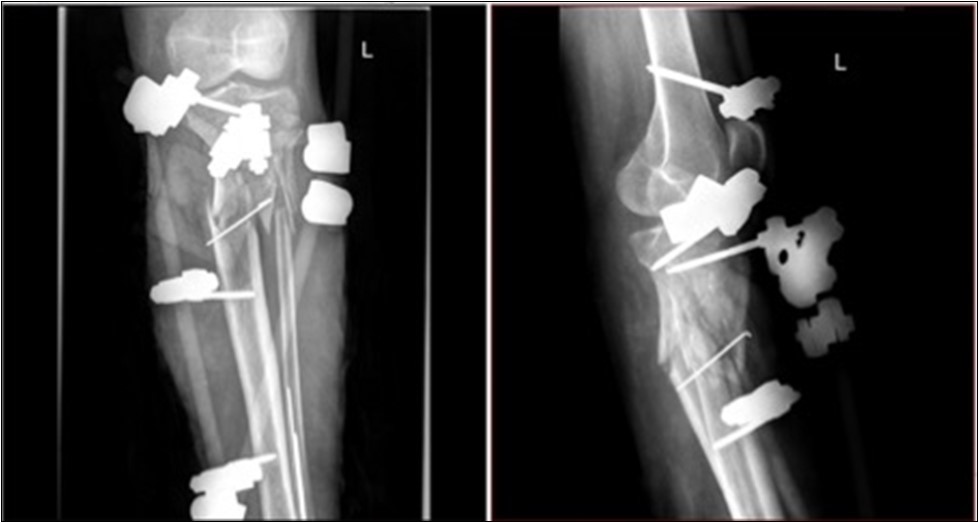
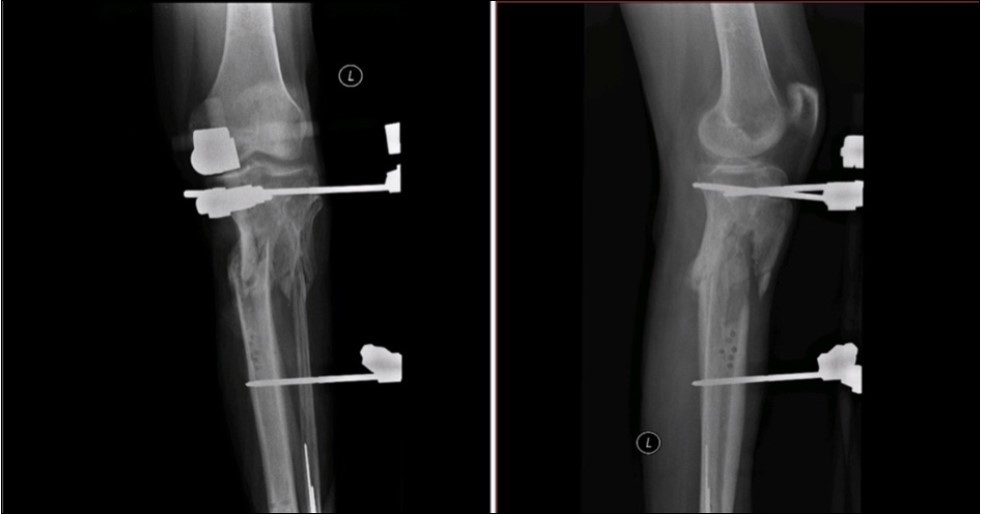
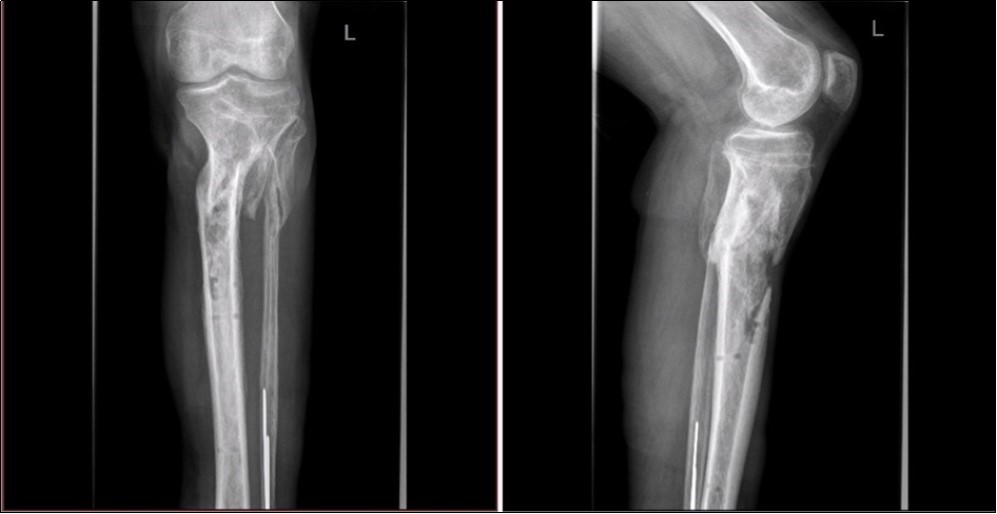
Case No.1 involves injuries to a 70 year old woman who was driven over by a bus wheel in the area of the tibia shaft. Primary diagnoses have been established as an open fracture of the tibia by Gustillo-Anderson IIIB 11. Laceration of soft tissue in central part of tibia. Other diagnoses of injury are fracture of tali et ossis calcanei, fracture of ossis metatarsi No.I, fracture of ossis cuneiformis medialis. Hypertension, hypercholesterolemia is related to personal amanesis. There was no injury to marginal vessels and nerves. Ischemia on the periphery or missing pulse was not detected and MESS absolute indication of amputation <7.1 If MESS score is greater than 7, we have to think about limb amputation. Table 1, Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14, Figure 15, Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18, Figure 19, Figure 20,Figure 21, Figure 22, Figure 23, Figure 24, Figure 25, Figure 26, Figure 27, Figure 28, Figure 29, Figure 30, Figure 31, Figure 32.
Table 1. MESS Absolute indication of amputation > 7| Energy | Low | 1 |
| Medium | 2 | |
| High | 3 | |
| Very High | 4 | |
| Ischemia | Perfused | 1 |
| Pulse absent | 2 | |
| Cool, Paralized, insansate | 3 | |
| Shock | SBP>90 | 0 |
| Transient | 1 | |
| Hypotension, Persistent Hypotension | 2 | |
| Age | <30 | 0 |
| 30-50 | 1 | |
| >50 | 2 |
Figure 1.22 January – primary surgical treatment in the operating room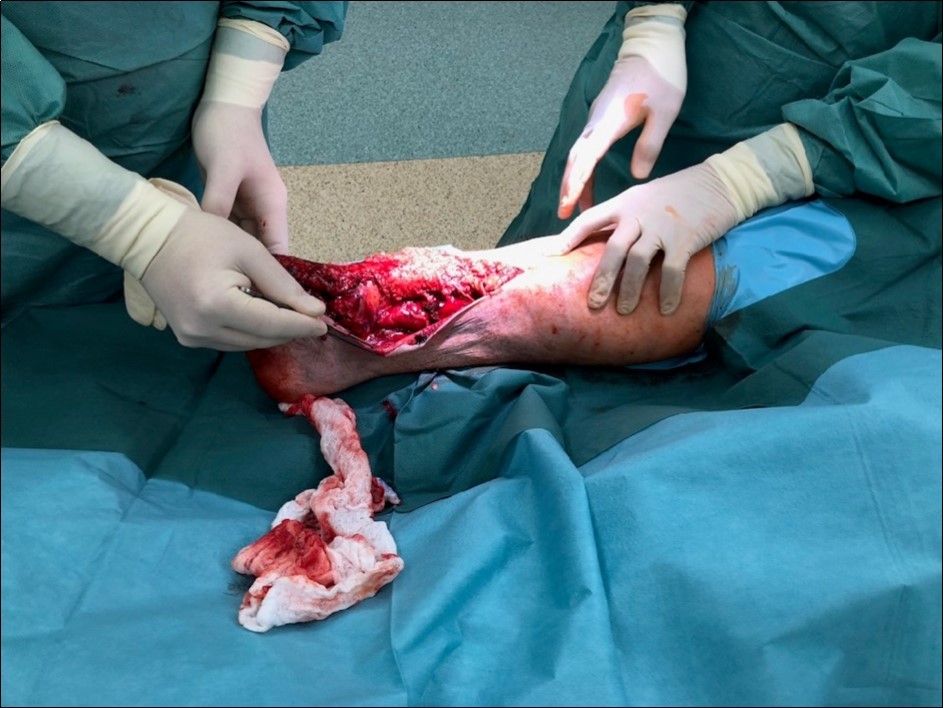
Figure 2.22 January – primary surgical treatment in the operating room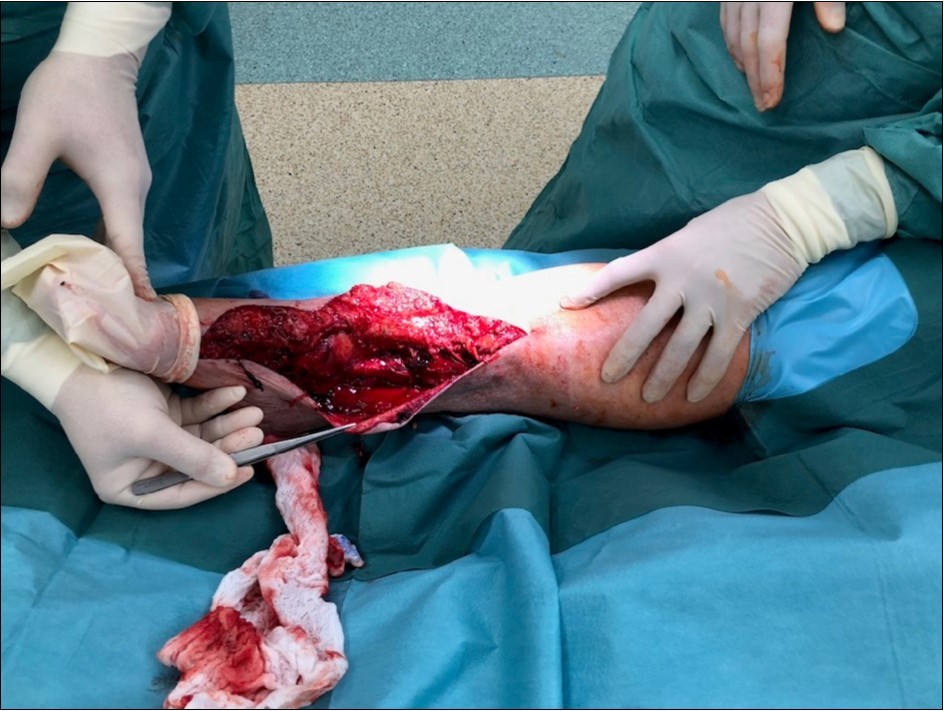
Figure 3.22 January – primary X-ray oblique splinter fracture of the tibia shaft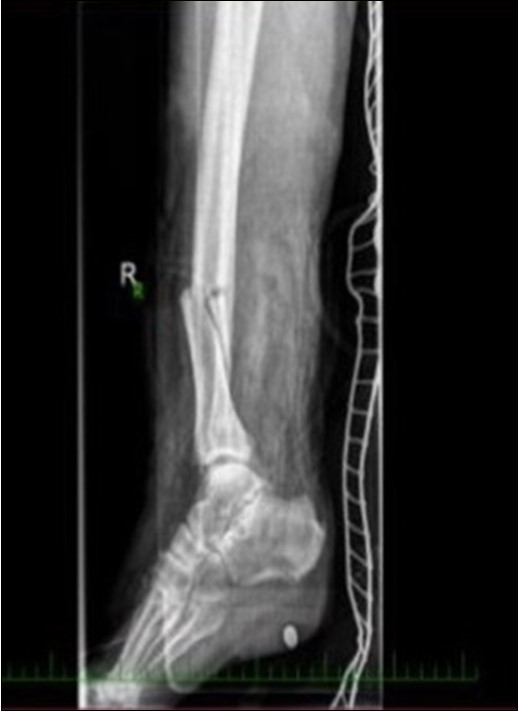
Figure 4.Debriteman and removal of macroscopic impurities Fracture stabilization using external fixator Reconstruction of soft tissue, subcutis and skin, necrectomy Installation of flushing lavage Covering defects with artificial skin – Syncryt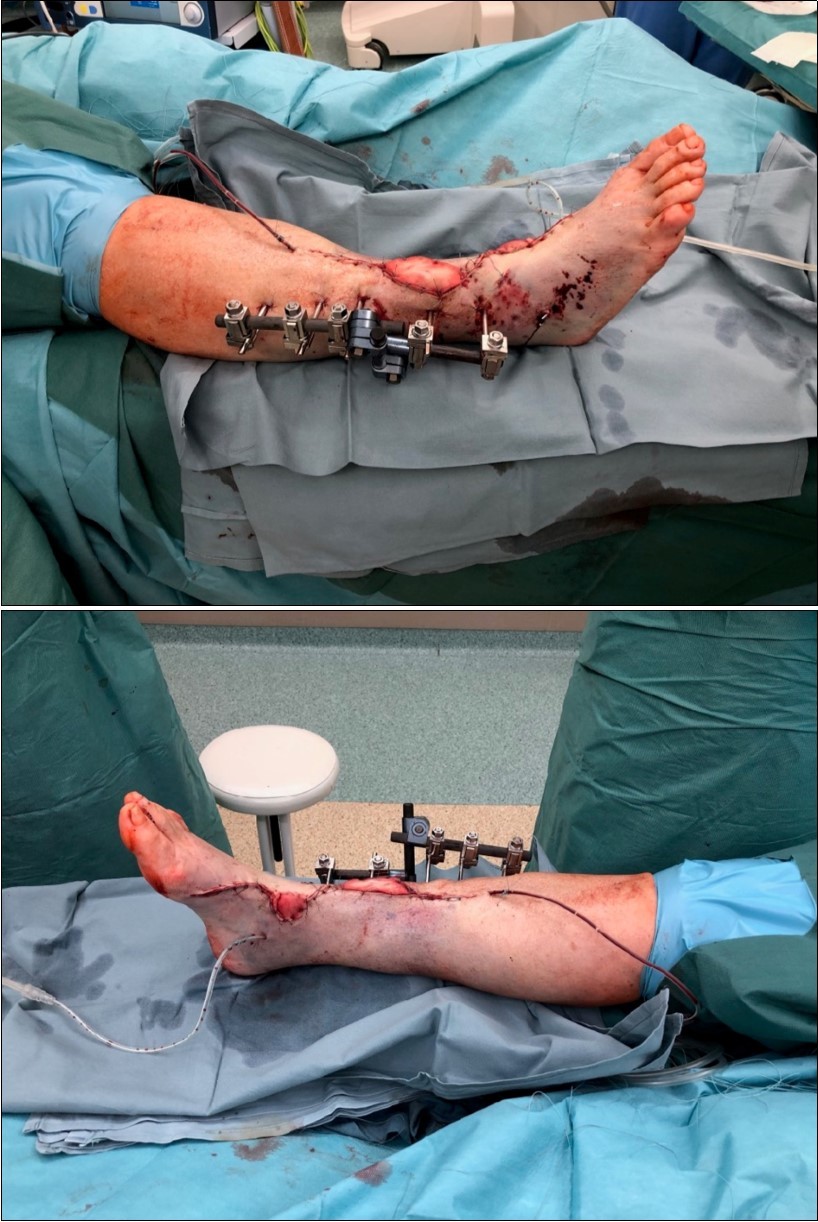
Figure 5.22 January – primary X-ray - Fracture stabilization using external fixator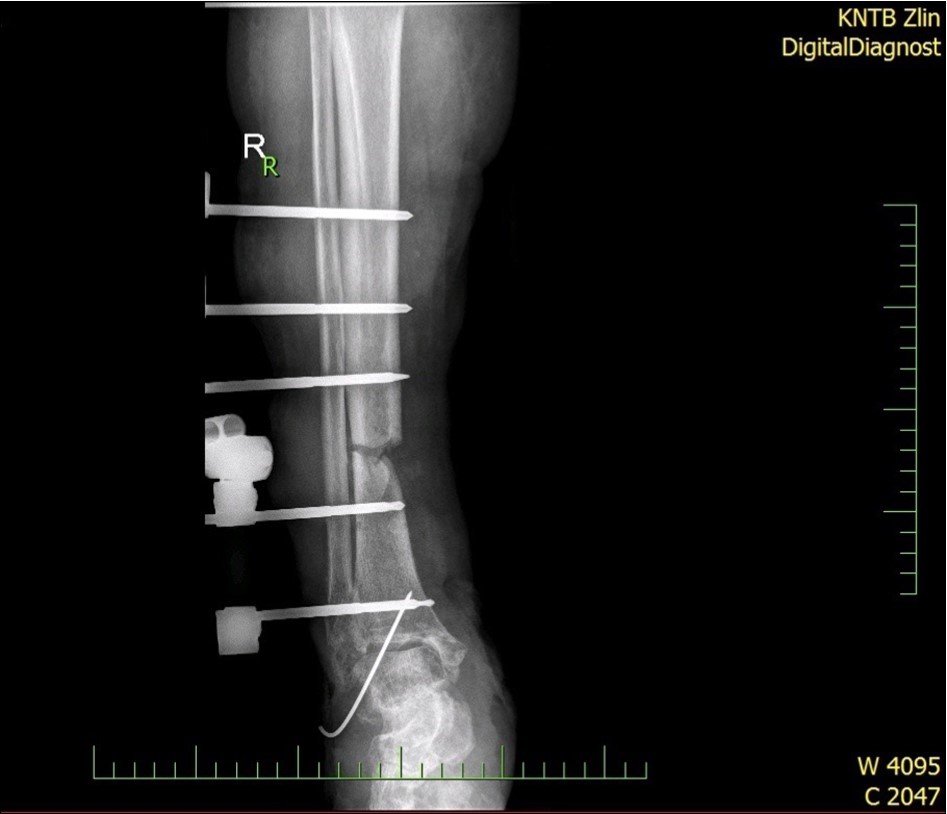
Figure 6.22 January – primary X-ray - Fracture stabilization using external fixator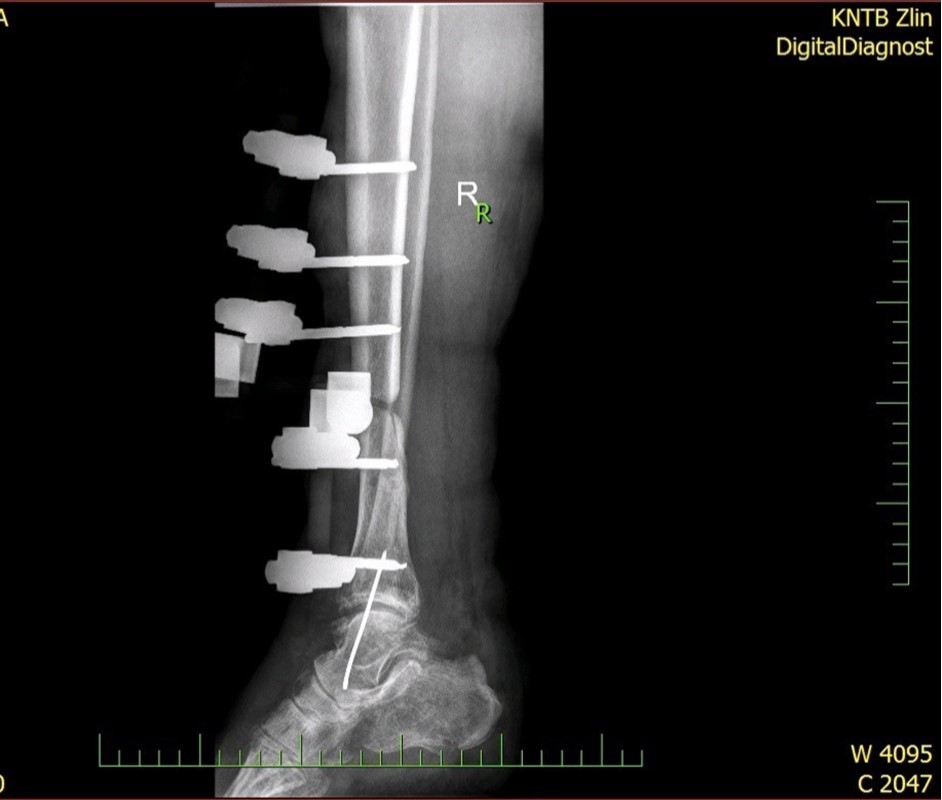
Figure 7.9 February. Extensive necrosis of skin and subcutis in the area of primary limb laceration. Progression of the skin necrosis line demarcation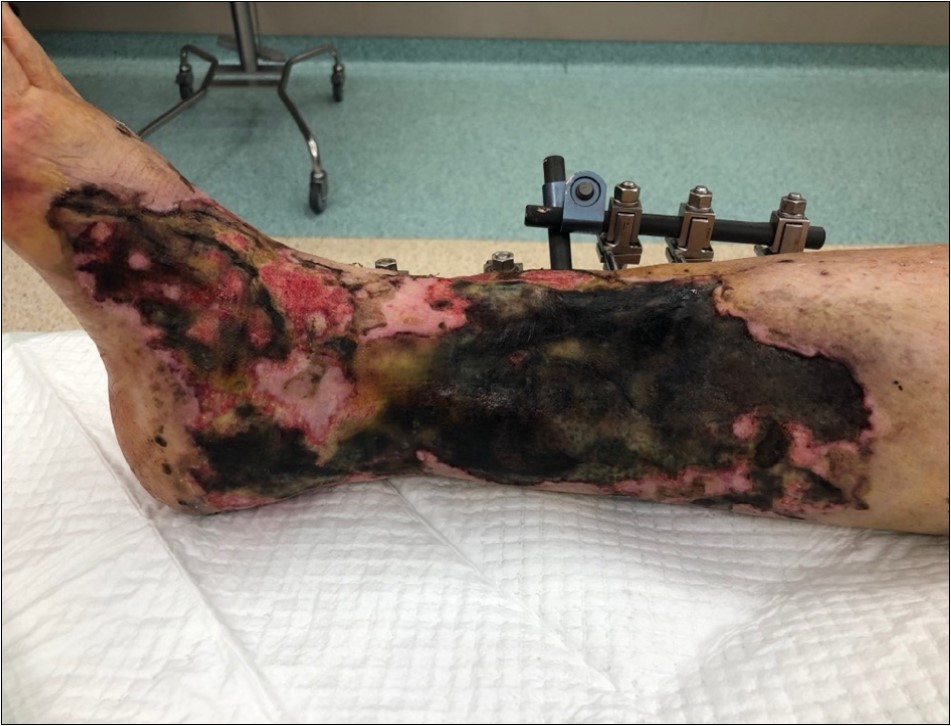
Figure 8.9 February. Extensive necrosis of skin and subcutis in the area of primary limb laceration. Progression of the skin necrosis line demarcation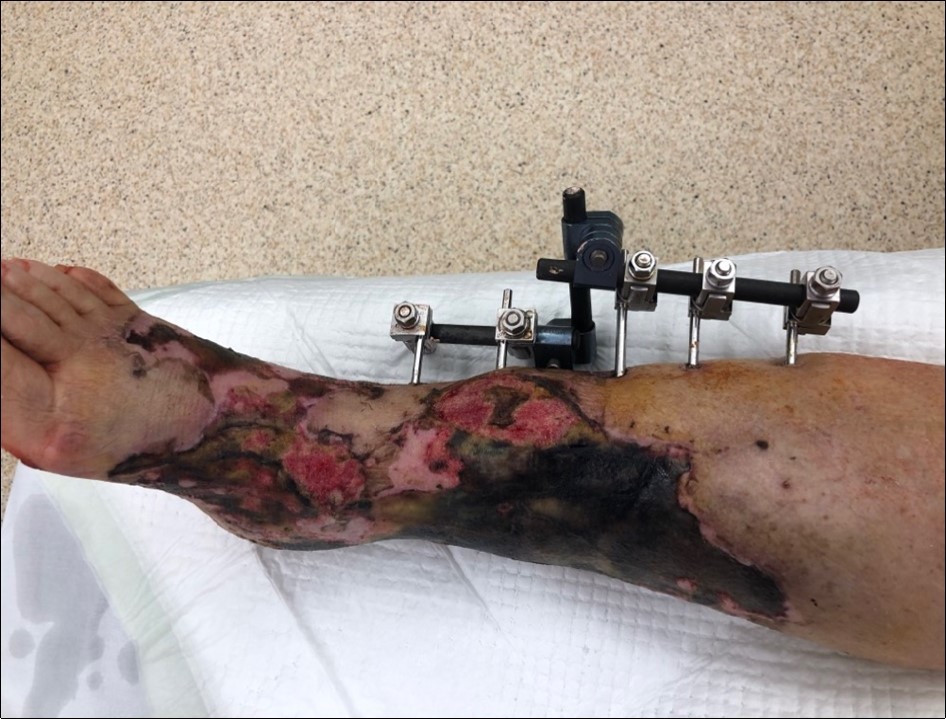
Figure 9.9 February. Extensive necrosis of skin and subcutis in the area of primary limb laceration. Progression of the skin necrosis line demarcation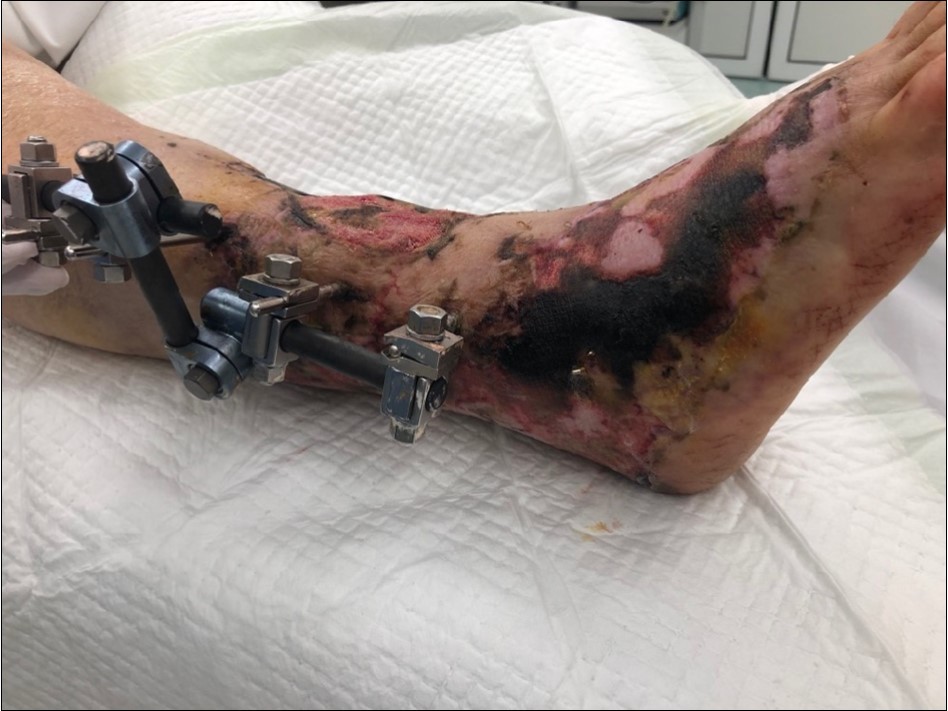
Figure 10.19 February. performed necrectomy, vitalization of subcutis, application negative pressure wound therapy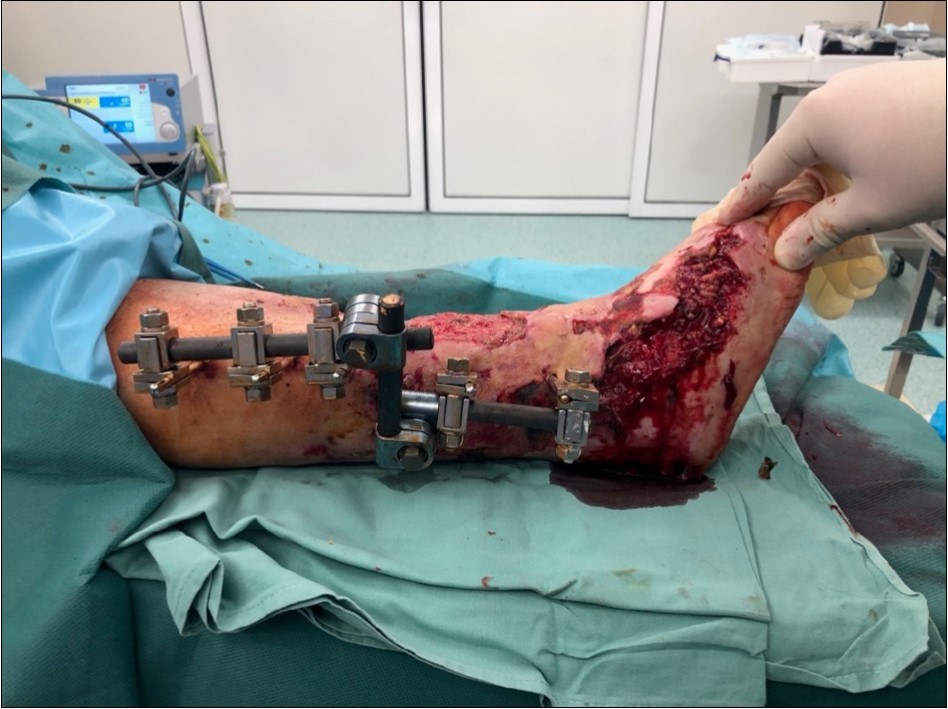
Figure 11.19 February. performed necrectomy, vitalization of subcutis, application negative pressure wound therapy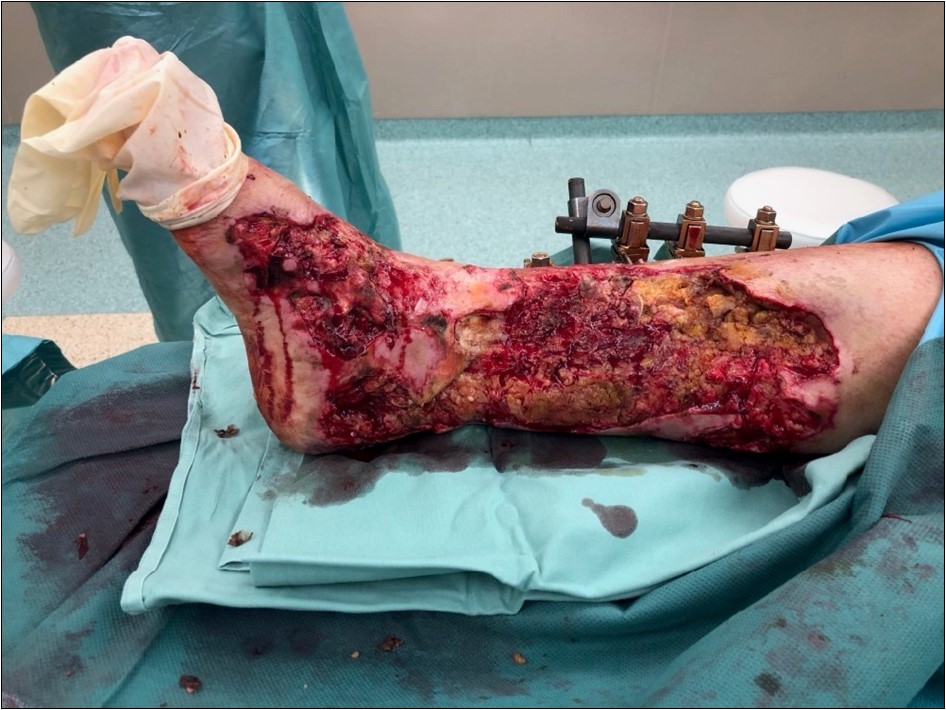
Figure 12.19 February. performed necrectomy, vitalization of subcutis, application negative pressure wound therapy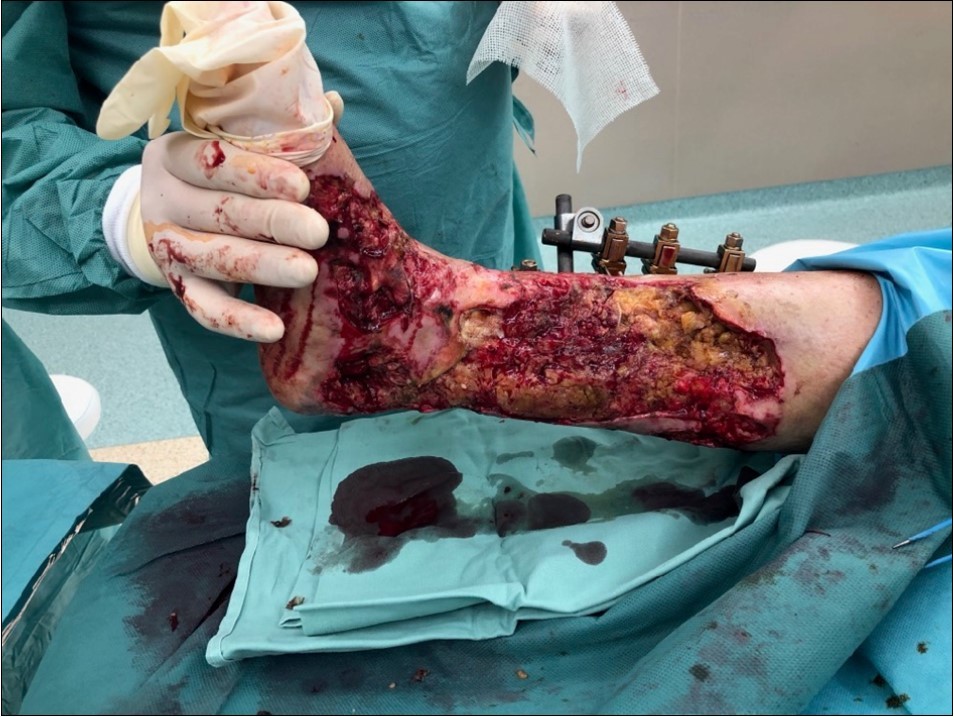
Figure 13.19 February. application of negative pressure wound therapy Vivano. application of polyurethane foam, foil, central port with tubing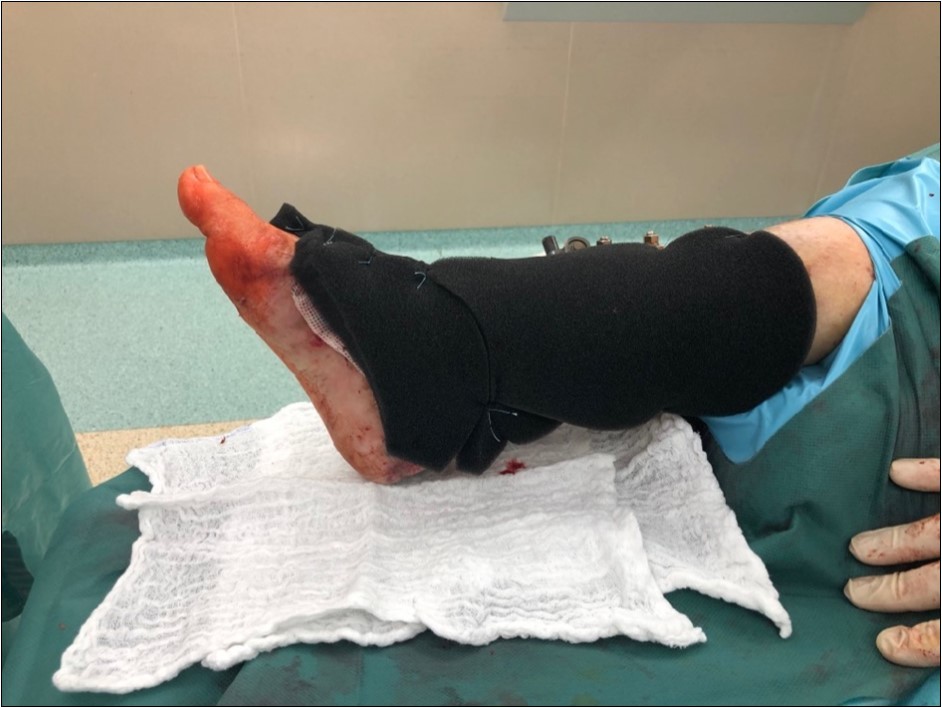
Figure 14.19 February. application of negative pressure wound therapy Vivano. application of polyurethane foam, foil, central port with tubing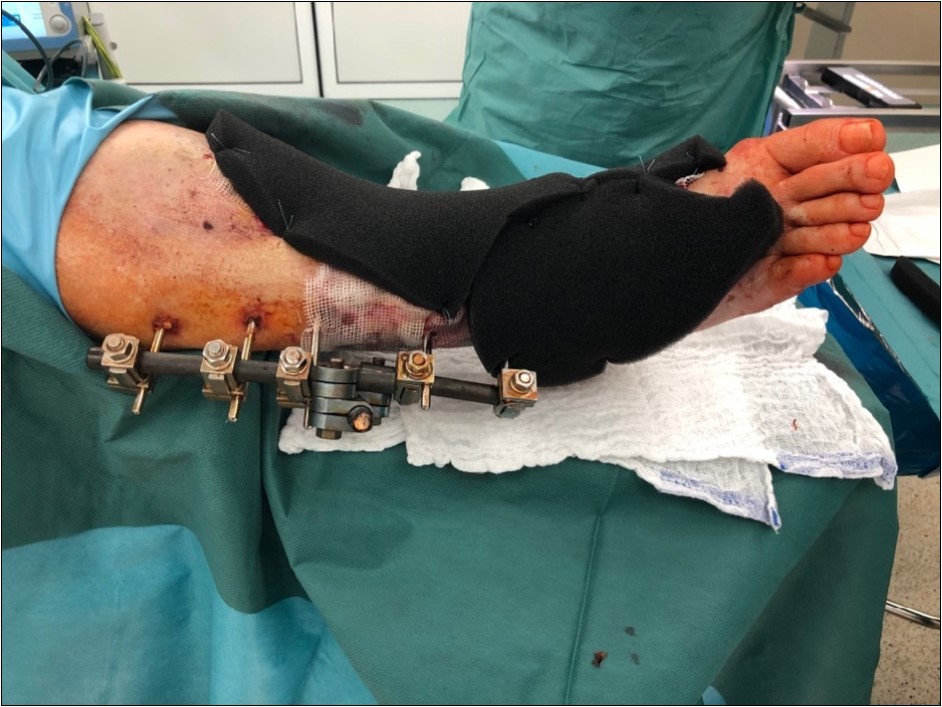
Figure 15.19 February. application of negative pressure wound therapy Vivano. application of polyurethane foam, foil, central port with tubing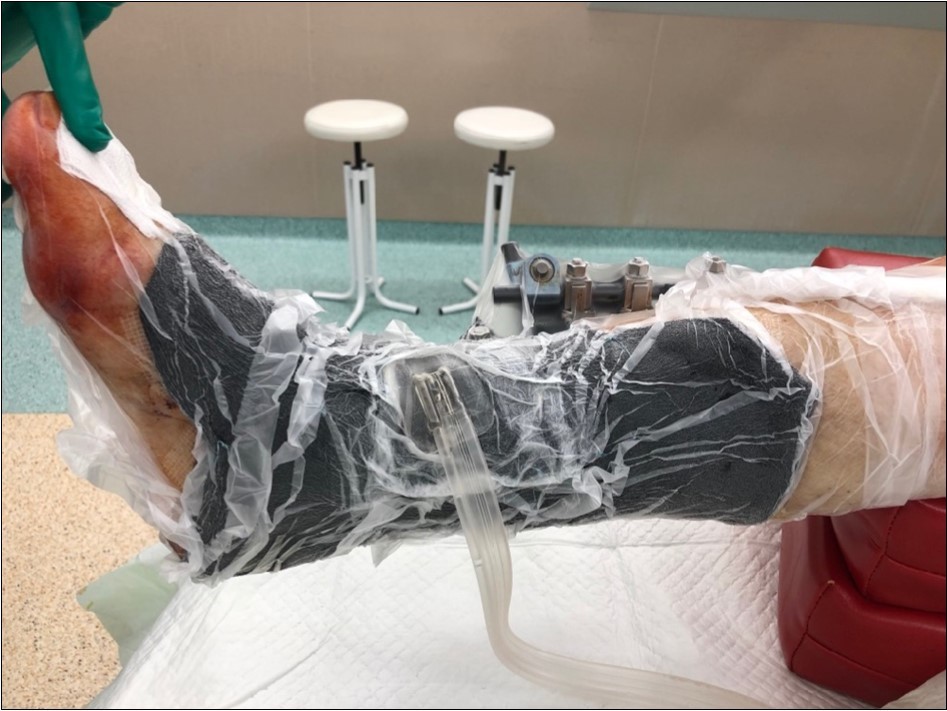
Figure 16.19 February. application of negative pressure wound therapy Vivano. application of polyurethane foam, foil, central port with tubing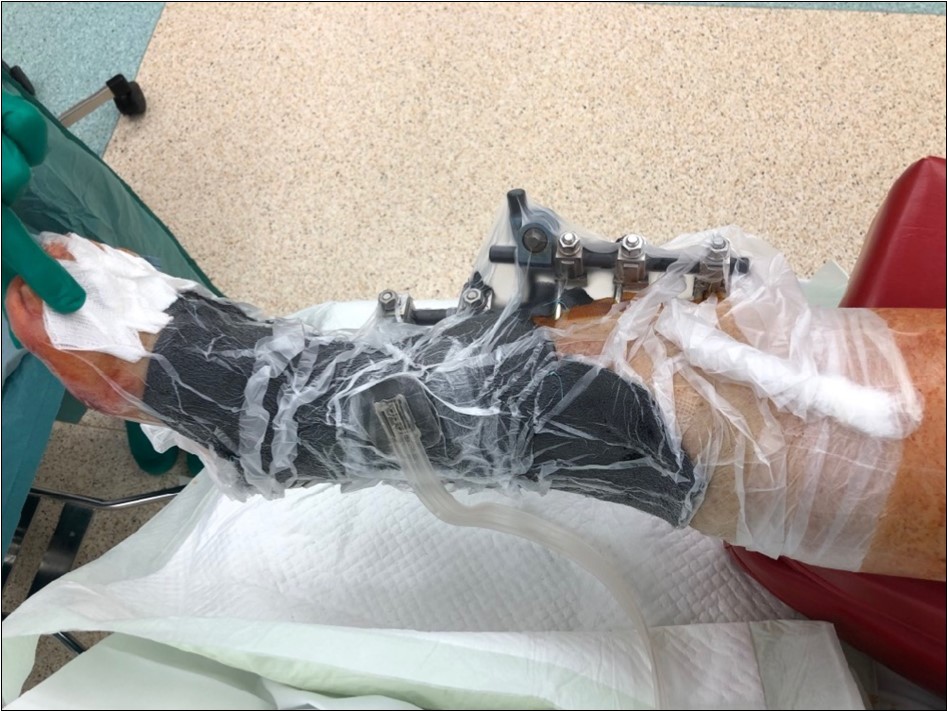
Figure 17.4 March - after one removing the vacuum therapy. demonstration of subcutaneous granulation. wound dressing changing every 5-6 days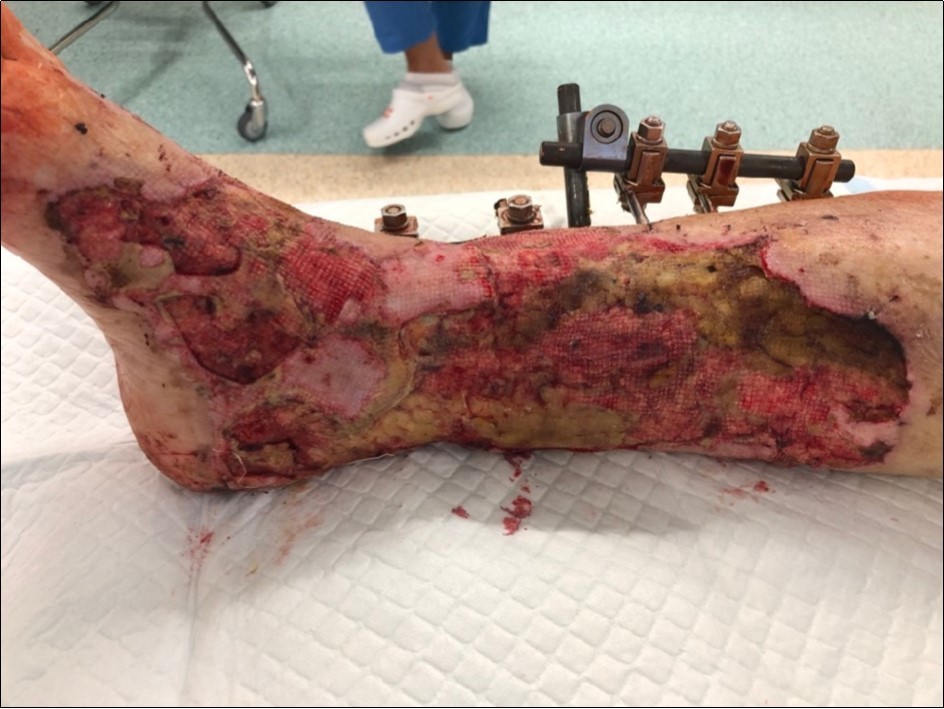
Figure 18.4 March - after one removing the vacuum therapy. demonstration of subcutaneous granulation. wound dressing changing every 5-6 days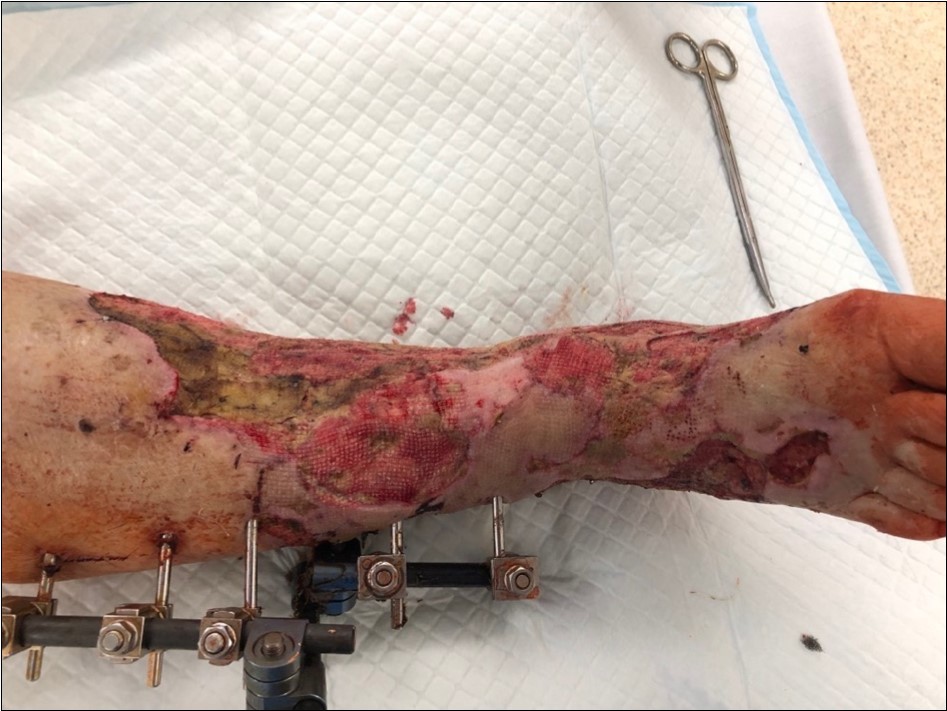
Figure 19.4 March - after one removing the vacuum therapy. demonstration of subcutaneous granulation. wound dressing changing every 5-6 days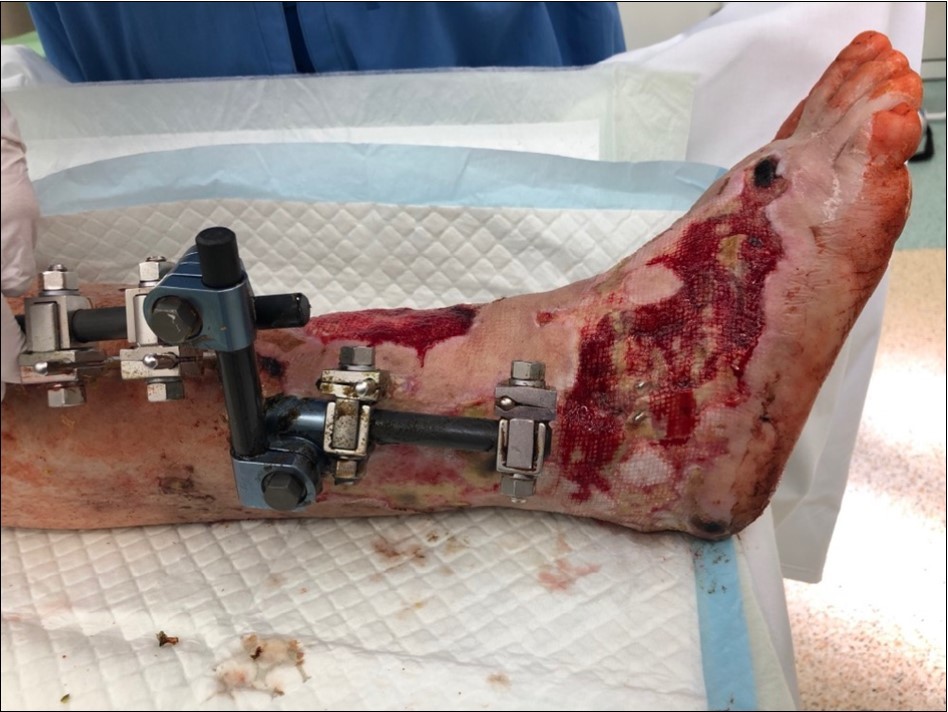
Figure 20.19 March. Defect of limb already clean with granulation ready for application of dermoepidermal graft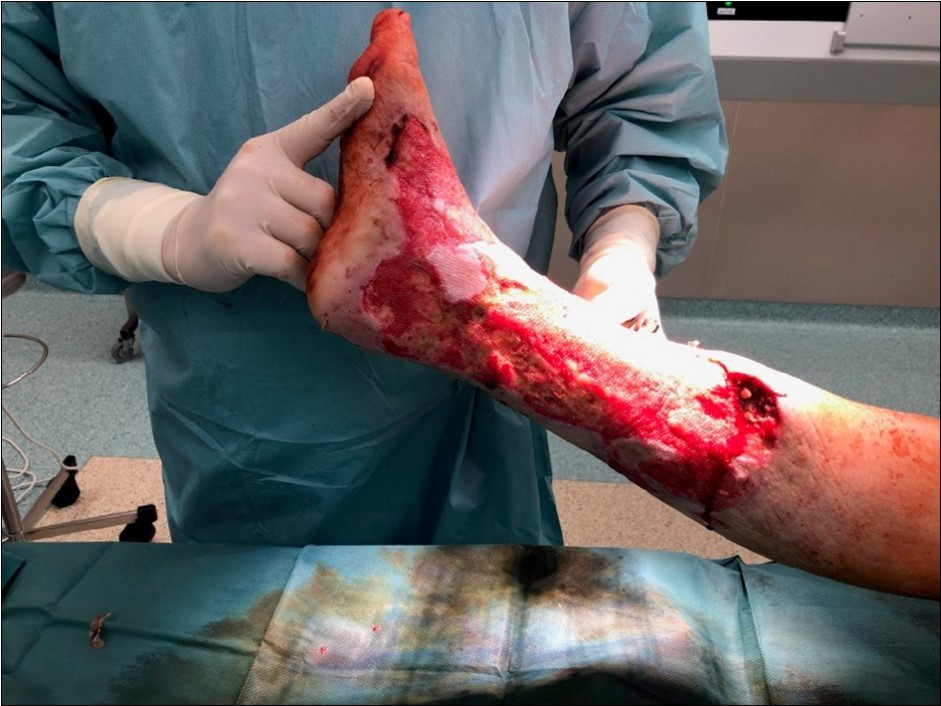
Figure 21.19 March. Defect of limb already clean with granulation ready for application of dermoepidermal graft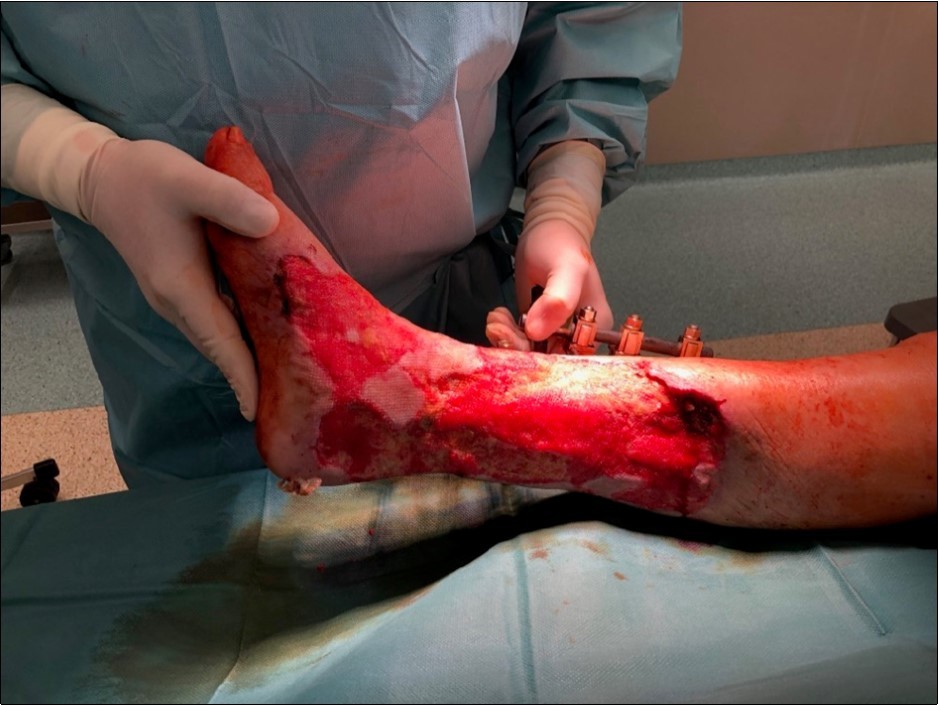
Figure 22.19 March. Defect of limb already clean with granulation ready for application of dermoepidermal graft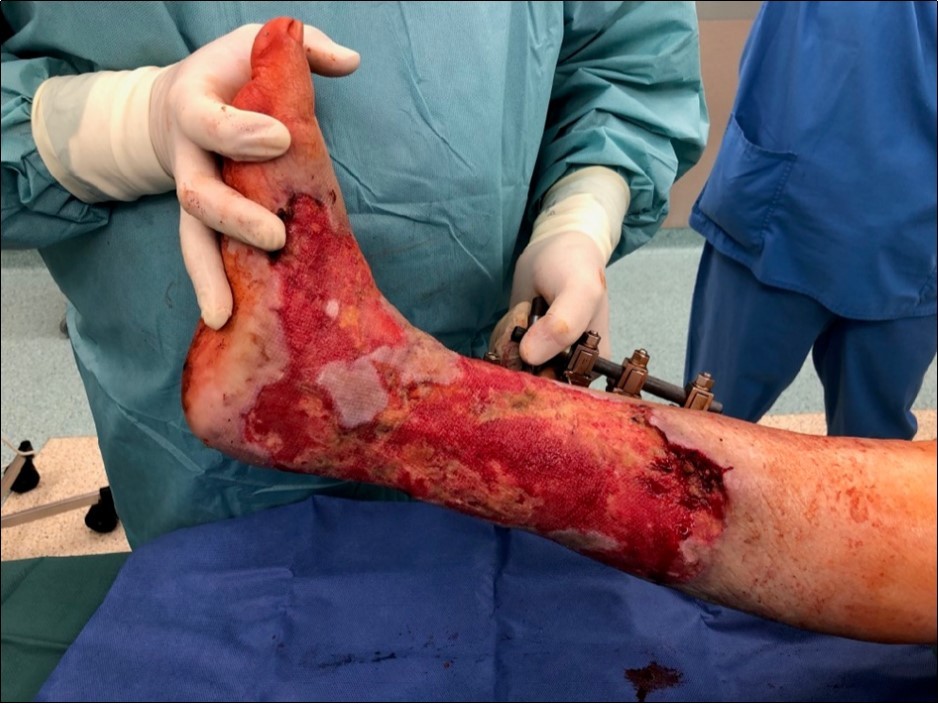
Figure 23.application of dermoepidermal graft with vacuum therapy of 90mmHg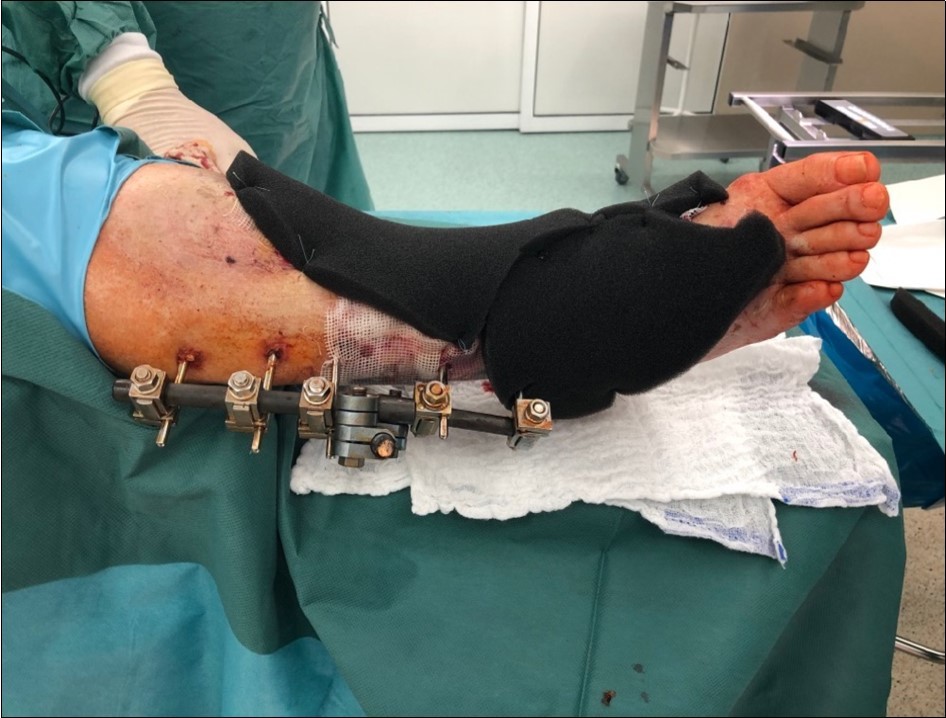
Figure 24.application of dermoepidermal graft with vacuum therapy of 90mmHg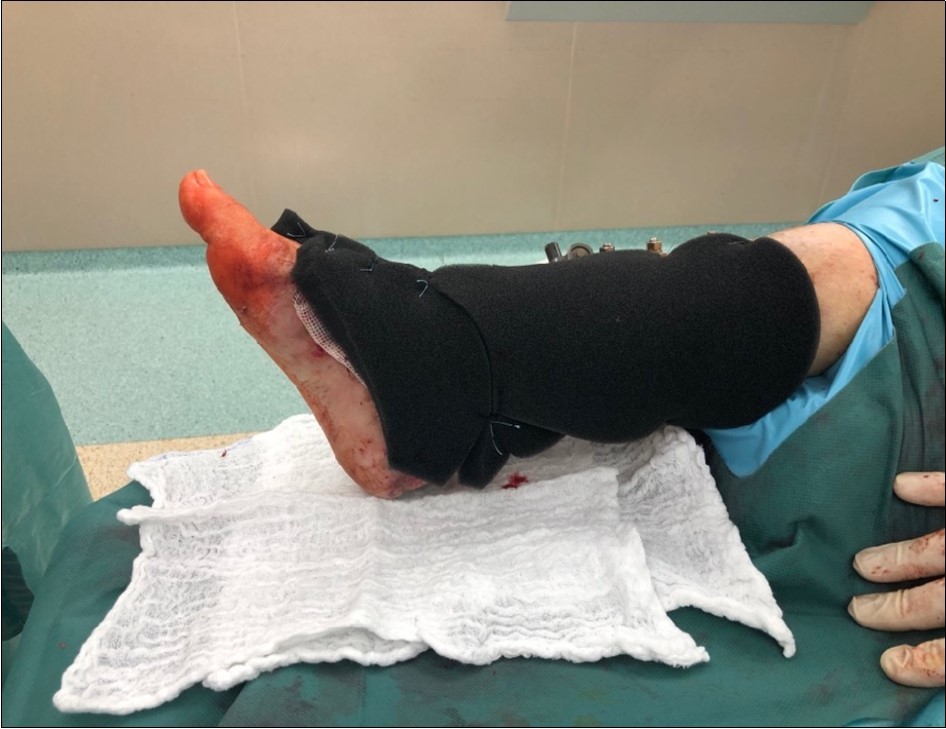
Figure 25.application of dermoepidermal graft with vacuum therapy of 90 mmHg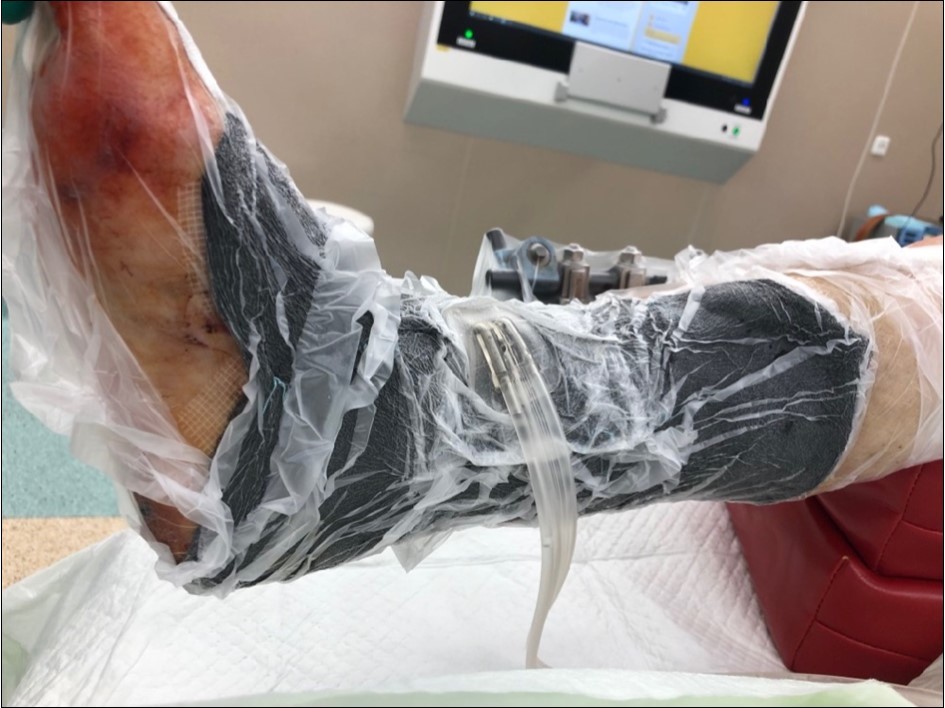
Figure 26.after removing the therapy. dermoepidermal graft successfully fixed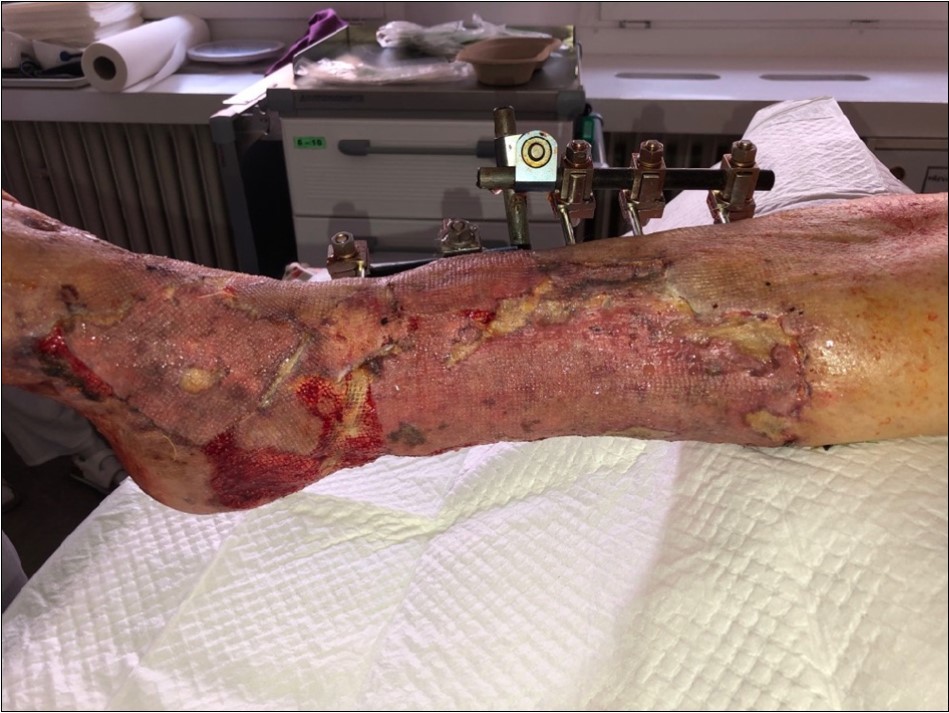
Figure 27.after removing the therapy. dermoepidermal graft successfully fixed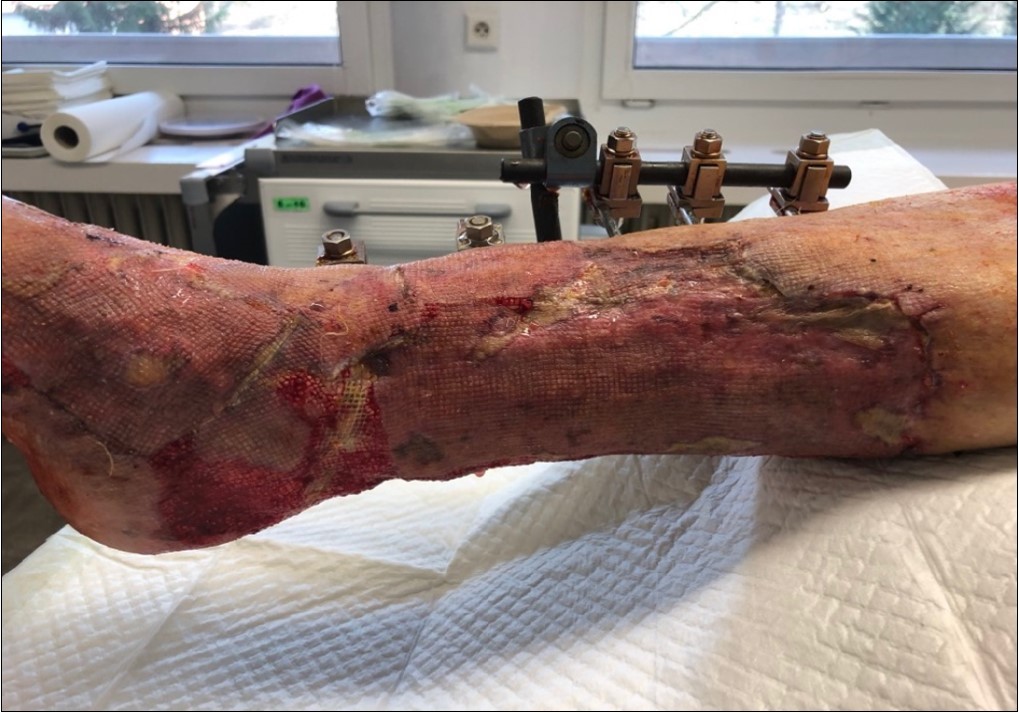
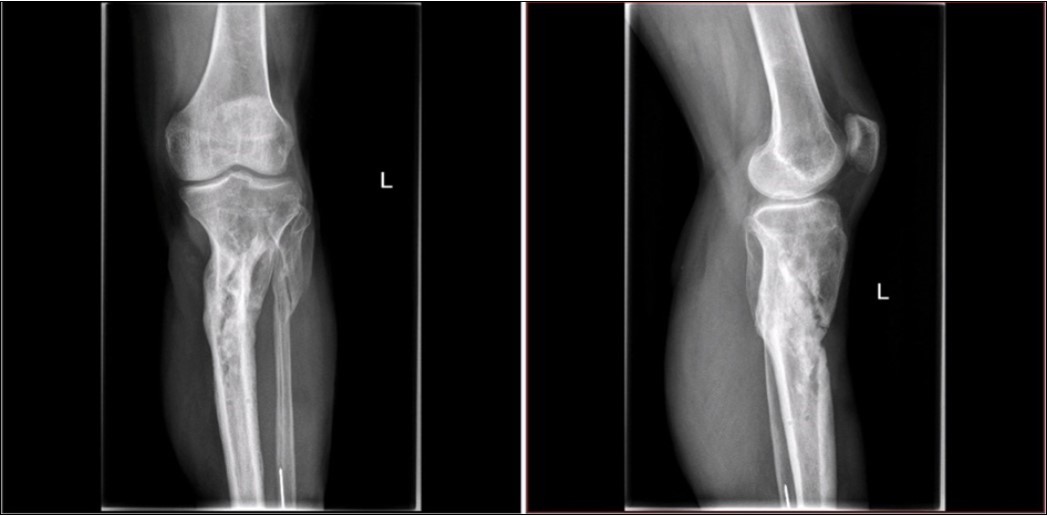
Figure 28.23 April. Surgery conversion of osteosynthesis. Removal external fixator and implantation intramedullary tibial nail. Gradual bone healing - last X-ray september 2019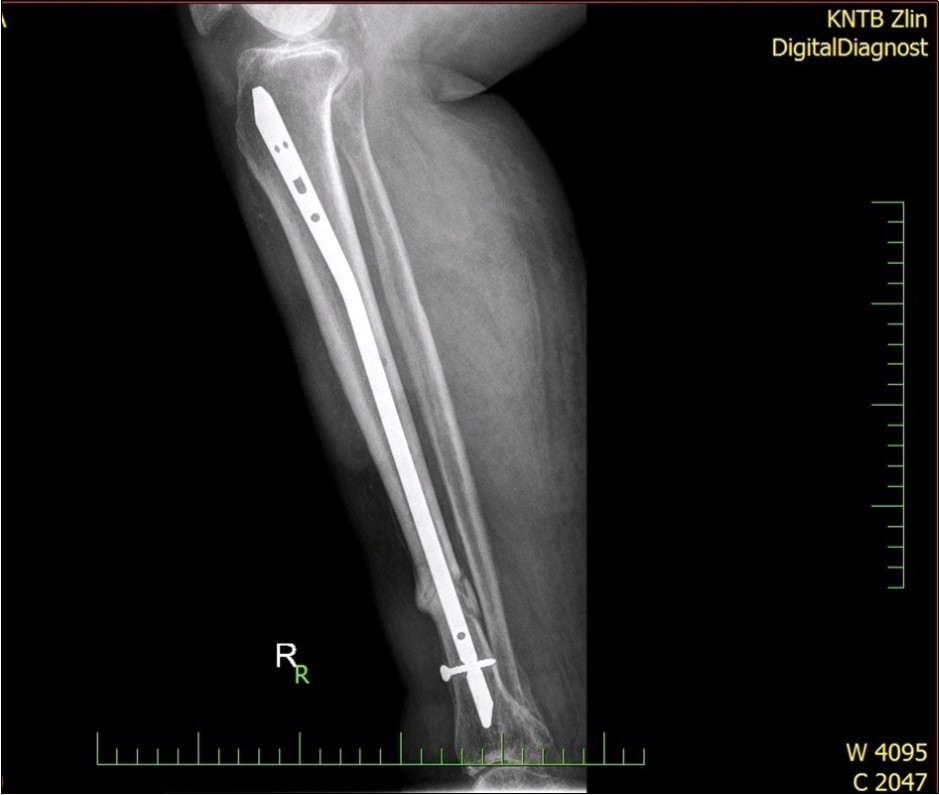
Figure 29.23 April. Surgery conversion of osteosynthesis. Removal external fixator and implantation intramedullary tibial nail. Gradual bone healing - last X-ray september 2019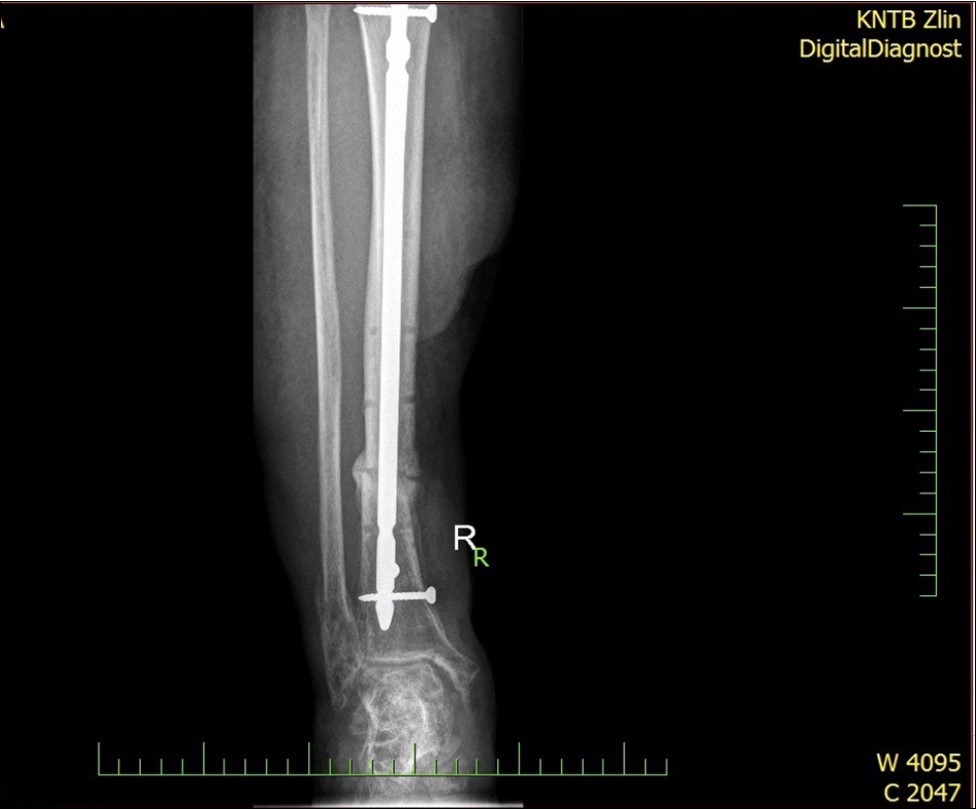
Figure 30.Gradual healing of small defects over the months may - august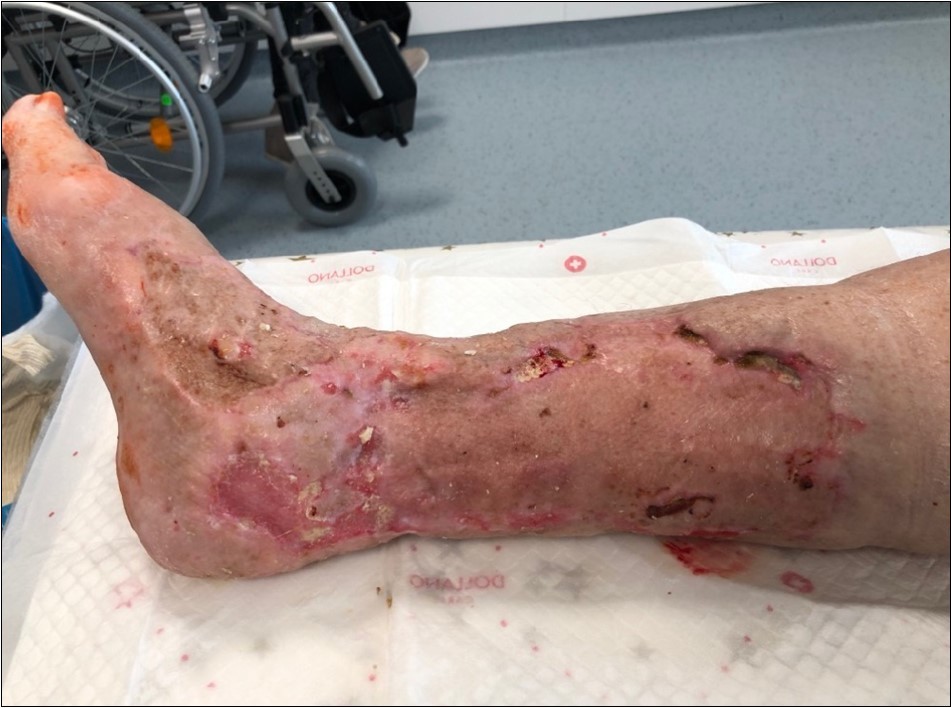
Figure 31.October 2019. skin cover completely healed. 8 months from the injury to heal soft tissues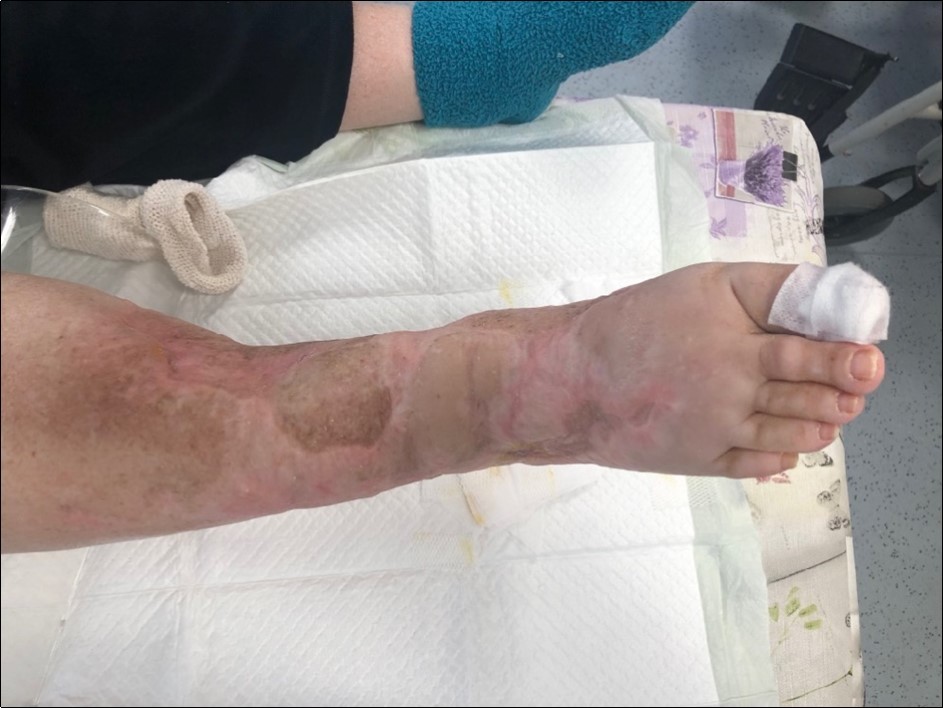
Figure 32.October 2019. skin cover completely healed. 8 months from the injury to heal soft tissues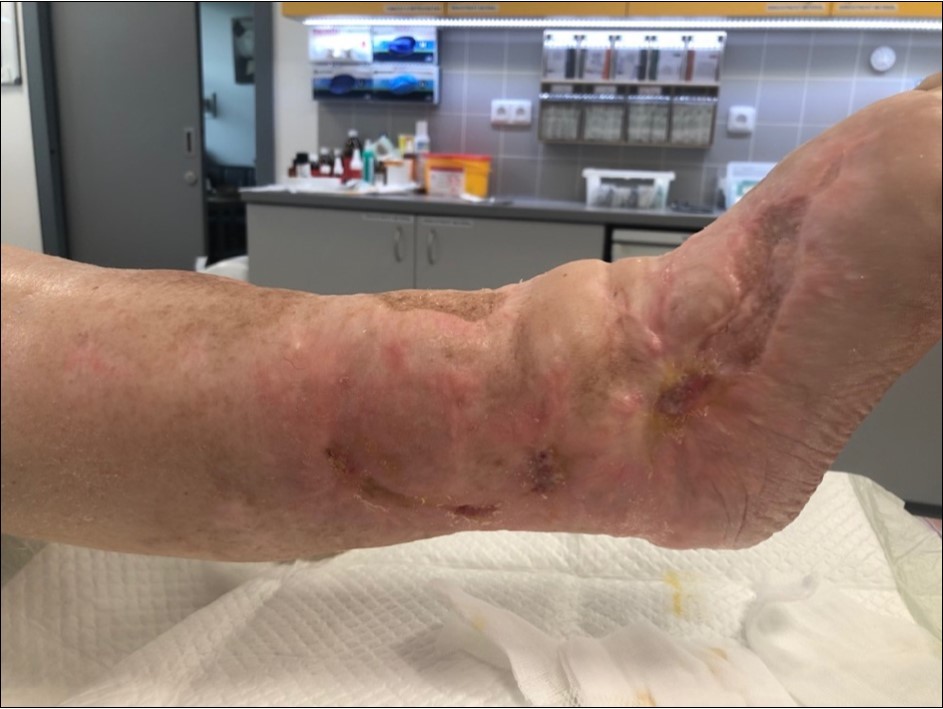
Case No.2 is about a man of 44 years old, where the injury caused by falling in ebrieta under the wheels of the bus. Primary acute treatment in the district hospital and then transferred to the Trauma Center of the Regional Hospital with open fracture of the tibia by Gustillo-Anderson IIIB 11. Extensive decollement of soft calf tissues up to the knee. Other diagnoses included the fracture of malleoli lateralis, acute hemorrhagic shock, traumatic shock, crash syndrome, acute alcohol intoxication.
Case No: 2
Male 44 years old
9.October 2015 - acute surgery
Revision of limb perfusion and pulsation of marginal vessels. There was no detected injury of marginal vessels and nerves. MESS Absolute indication of amputation <7
Revision of soft tissue - extensive contusolaceration of the lower limb from the Achilles tendon through the whole calf to the medial side of the thigh - circular detachment of the skin and subcutis from the fascia, macroscopic contamination.
Application of external fixation and Ki wires to stabilization of fragments.
Reconstruction of the skin cover - excision of necrotic parts, covering defects using artificial skin Synkryt. Figure 33, Figure 34, Figure 35, Figure 36, Figure 37, Figure 38, Figure 39, Figure 40, Figure 41, Figure 42, Figure 43, Figure 44, Figure 45, Figure 46, Figure 47, Figure 48, Figure 49, Figure 50.
Figure 33. X-ray documentation of the whole treatment of tibia fracture. External fixation was used throughout the treatment until bone was healed. From 9.October 2015 to 2.February 2017
Figure 34.After 2 weeks. Progression of the skin necrosis line demarcation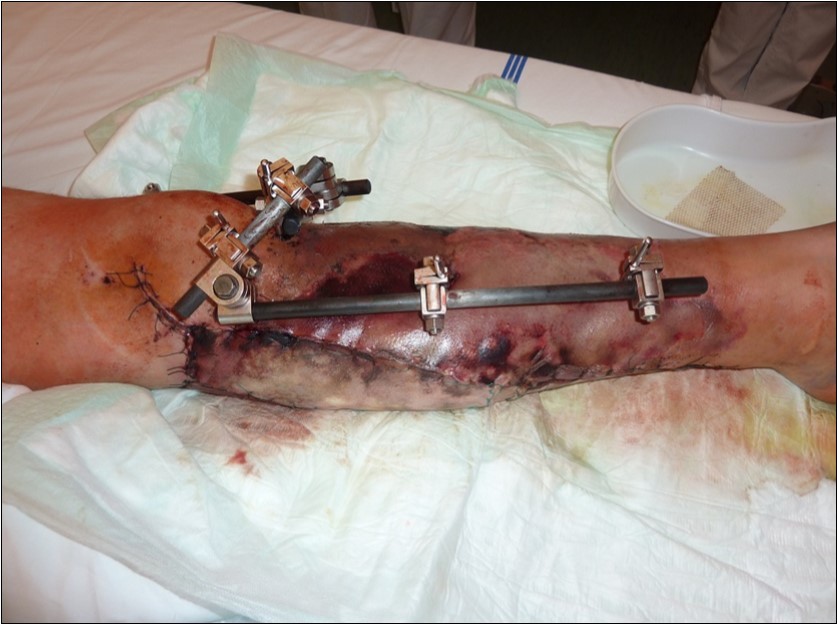
Figure 35.After 2 weeks. Progression of the skin necrosis line demarcation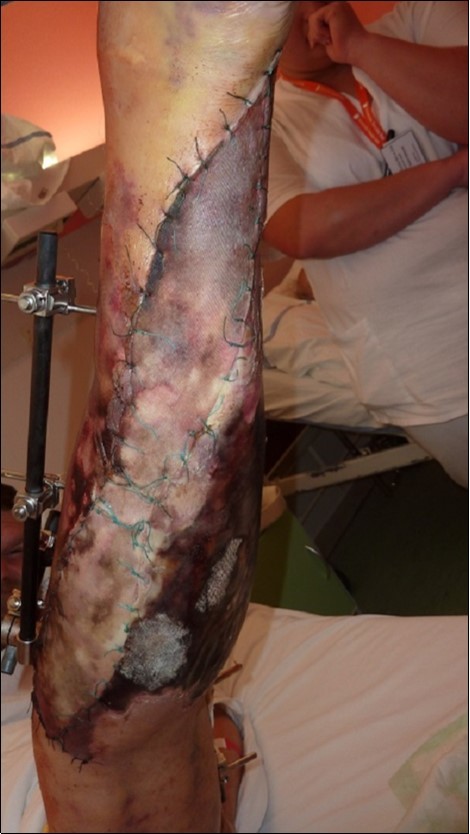
Figure 36.After 2 weeks. Progression of the skin necrosis line demarcation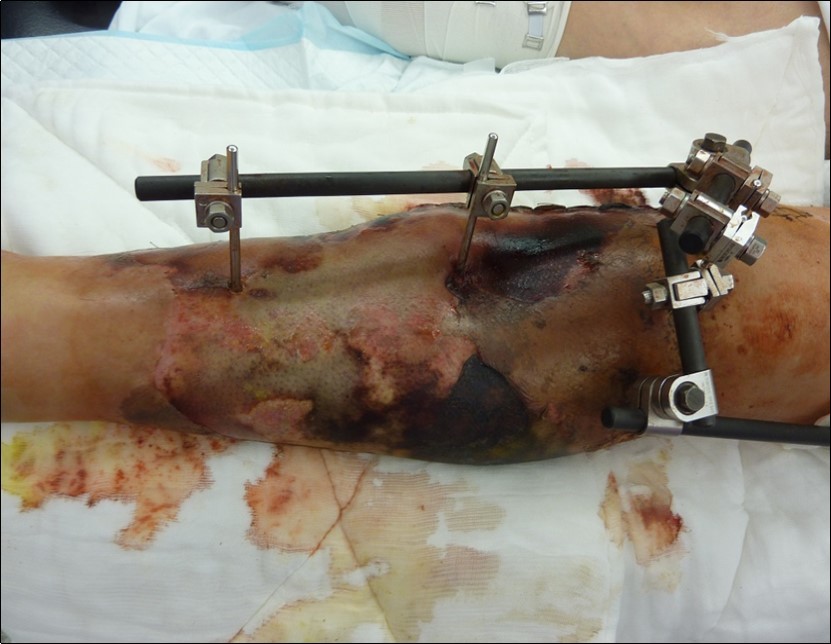
Figure 37.After 2 weeks. Progression of the skin necrosis line demarcation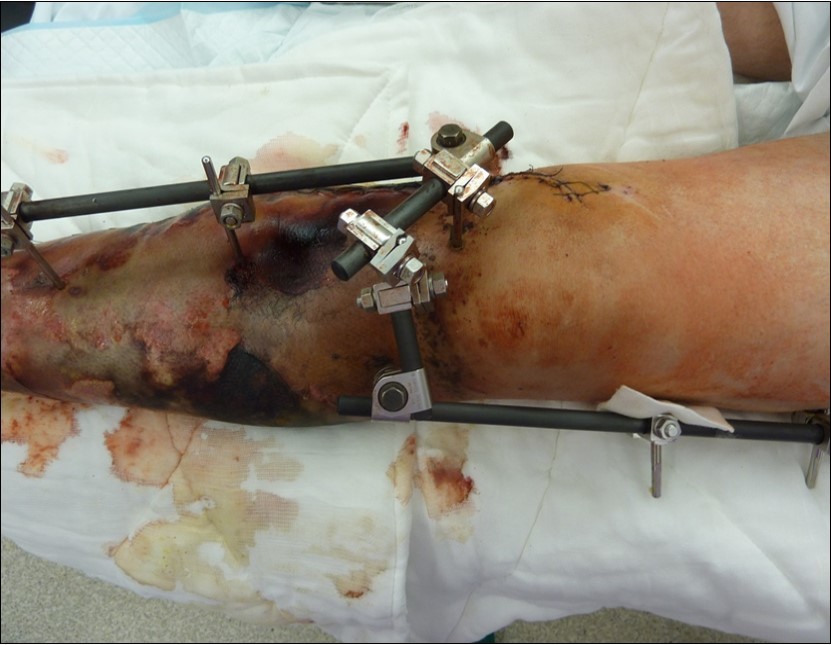
Figure 38.After 2 weeks. Progression of the skin necrosis line demarcation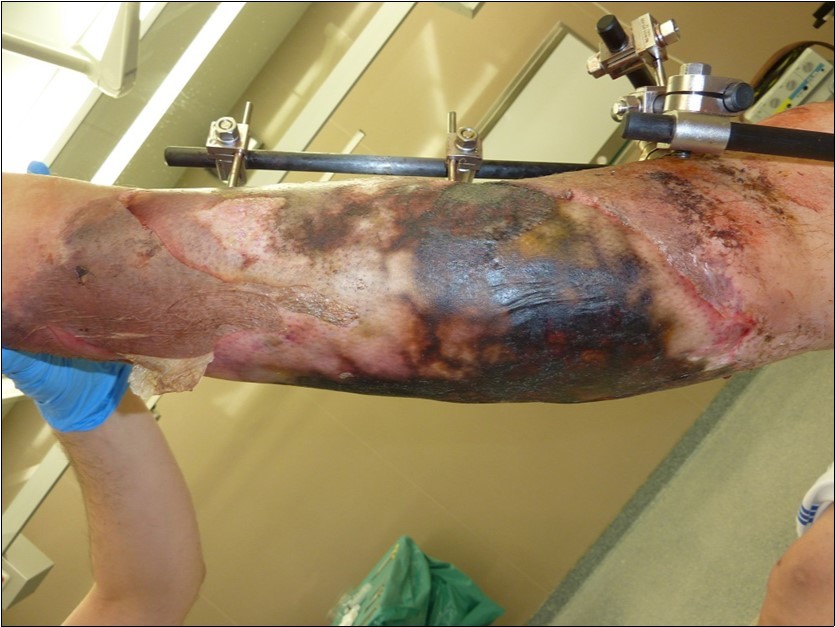
Figure 39.After 2 weeks. Progression of the skin necrosis line demarcation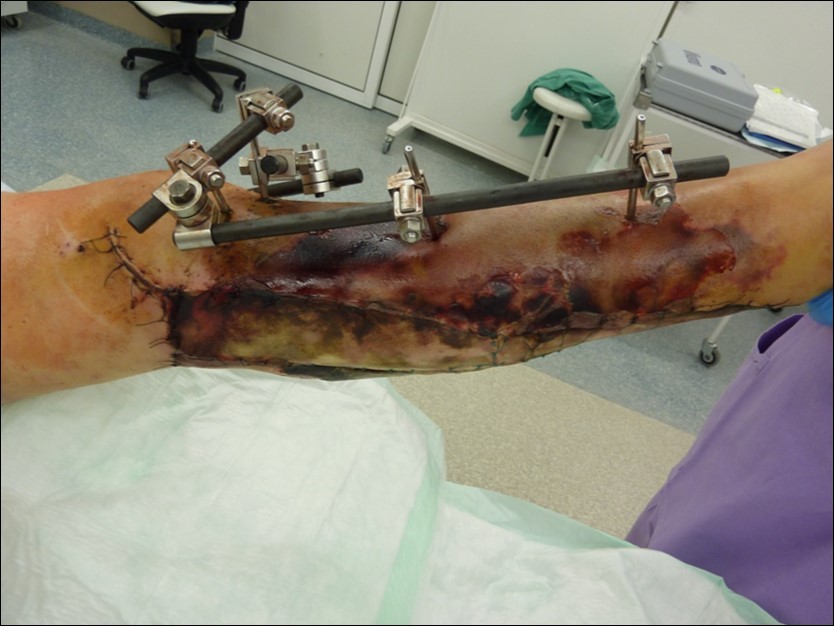
Figure 40.After 3 weeks performed necrectomy, vitalization of subcutis, application negative pressure wound therapy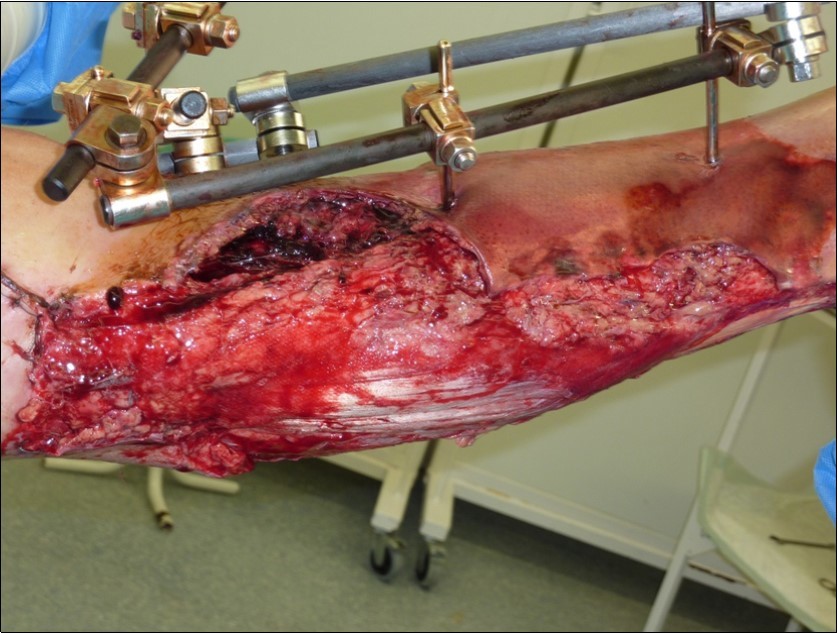
Figure 41.Picture of dressing changing of negative pressure woud therapy after 5weeks. demonstration of subcutaneous granulation. wound dressing changing every 5-6 days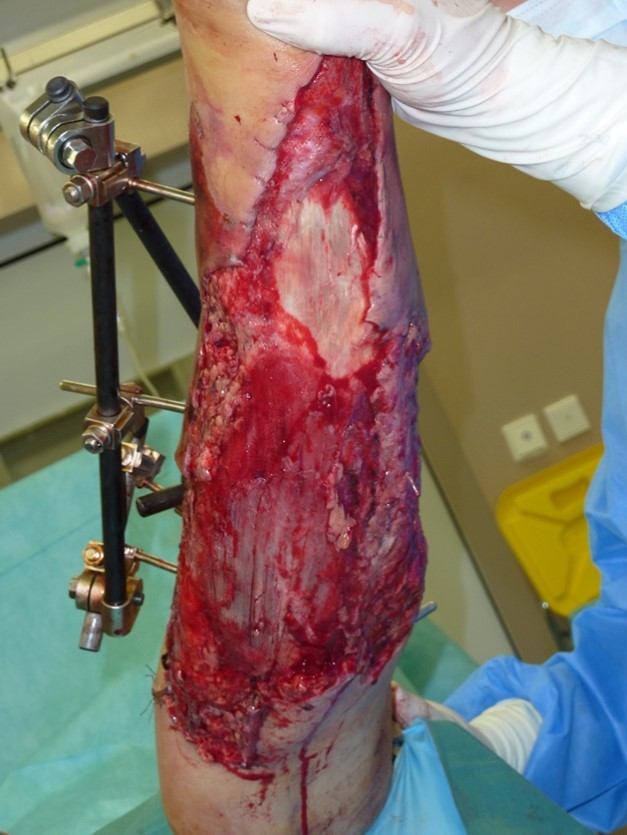
Figure 42.Dressing changing negative pressure woud therapy after 5 weeks. demonstration of subcutaneous granulation. wound dressing changing every 5-6 days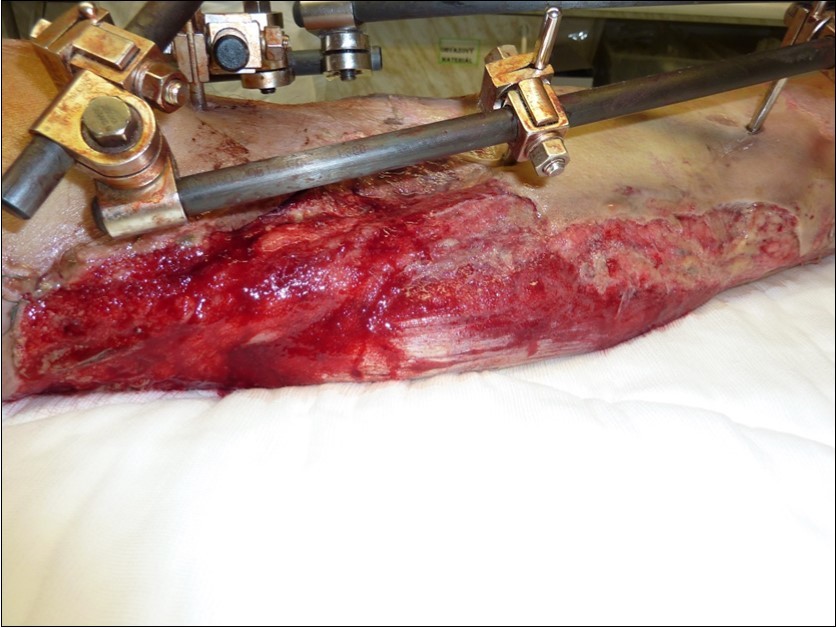
Figure 43.Dressing changing negative pressure woud therapy after 7 weeks. advanced granulation suitable for application of dermoepidermal graft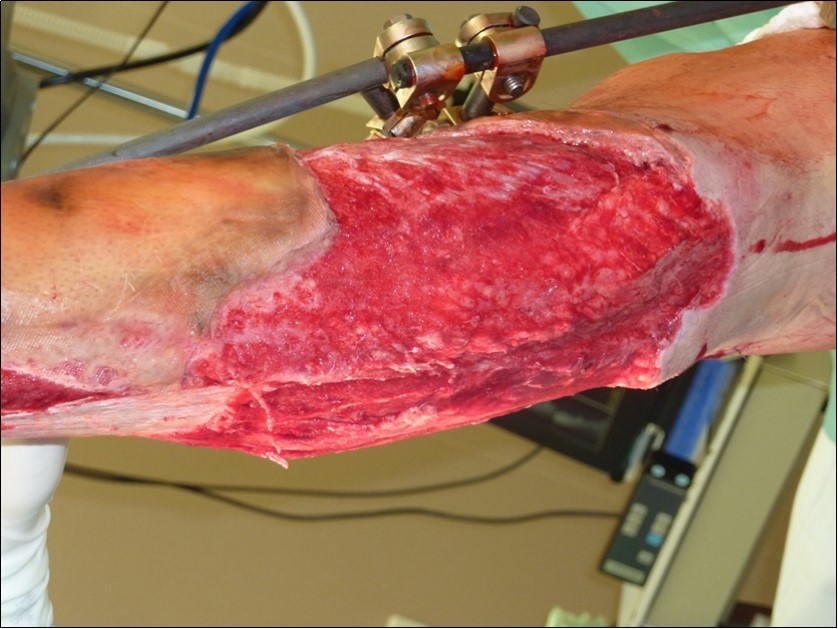
Figure 44.Dressing changing negative pressure woud therapy after 7 weeks. advanced granulation suitable for application of dermoepidermal graft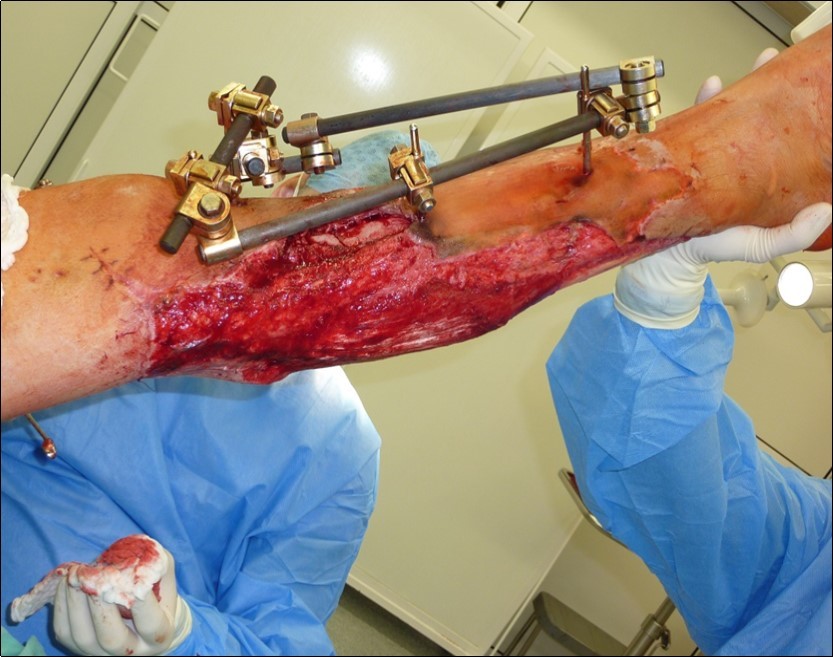
Figure 45.Application of dermoepidermal graft in individual steps from December 2015 to January 2016. use of vacuum therapy with good graft fixation and graft drainage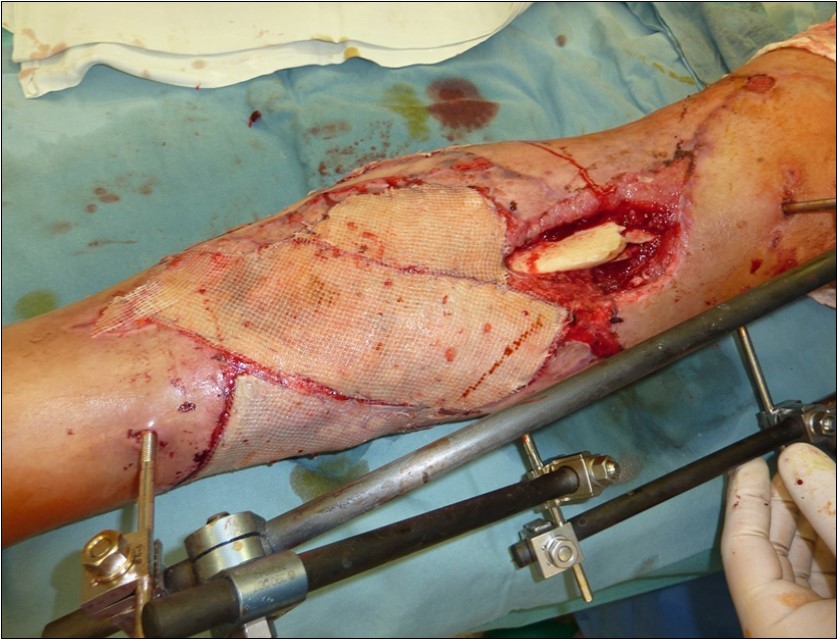
Figure 46.Application of dermoepidermal graft in individual steps from December 2015 to January 2016. use of vacuum therapy with good graft fixation and graft drainage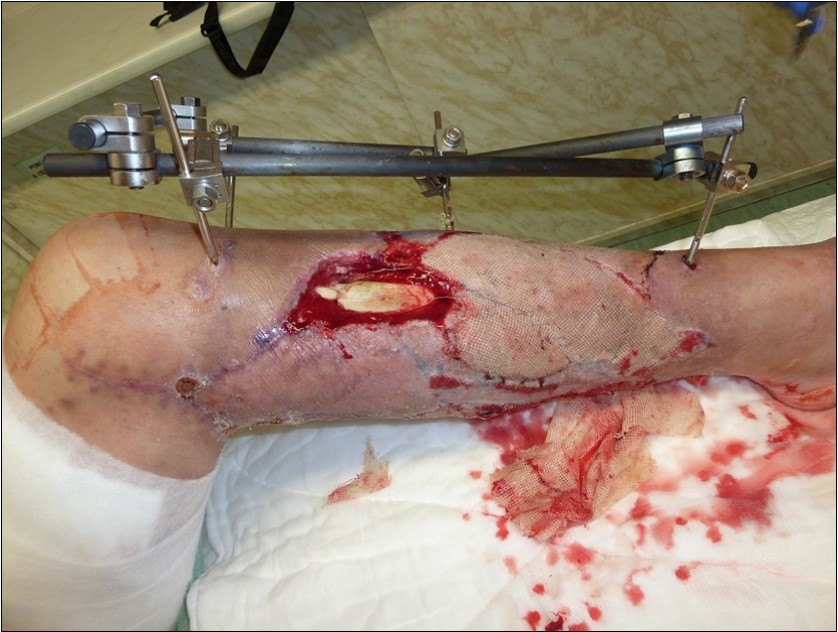
Figure 47.January 2016. resection of the tibial avital cortica and resuture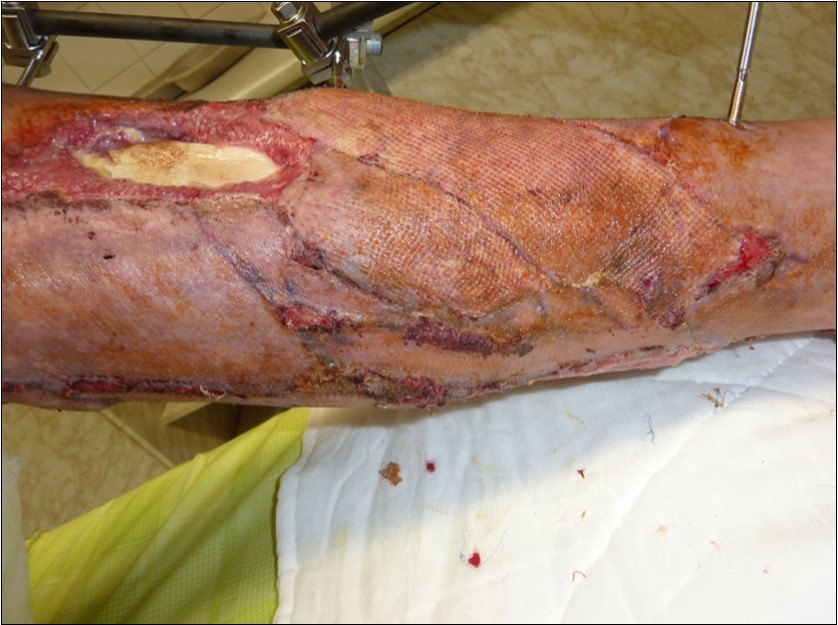
Figure 48.January 2016. resection of the tibial avital cortica and resuture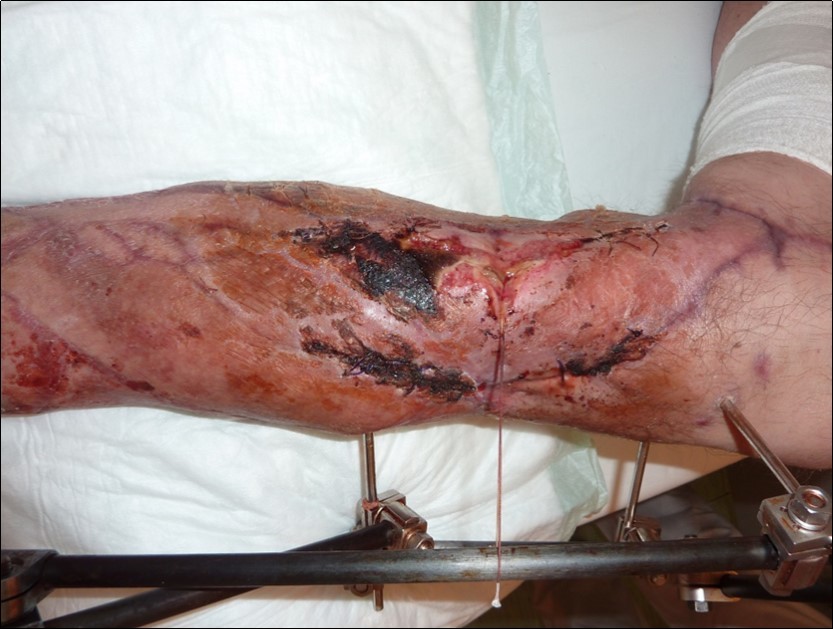
Figure 49.Jun 2016. skin cover completely healed. 9 months from the injury to heal soft tissues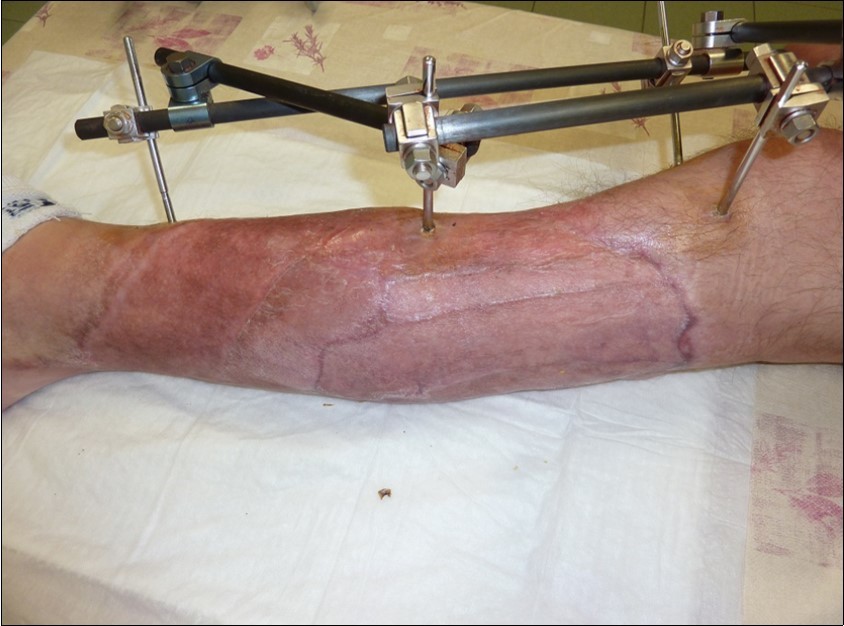
Figure 50.Skin cover completely healed. 9 months from the injury to heal soft tissues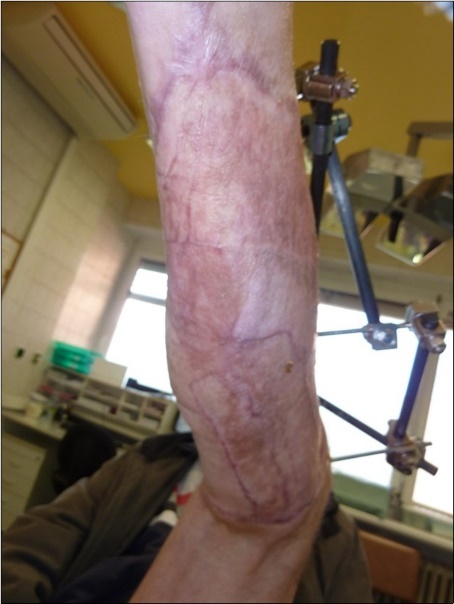
Results
Both cases of treatment open tibial fracture using NPWT have been cured successfully. The median duration of treatment was 8.5 months. The case report No.1., old lady was cured of skin cover and skeleton in 8 months. The case report No.2., 44 years man was heal in 9 months but his soft tissue injury was more extensive. Standard ATB procedures were used during treatment.
Individual photos present how quickly and effectively NPWT can help heal a soft tissue defect. The use of this therapy was essentially underestimated until the skin cover healed. A case report of NPWT confirms, that treatment of severe limb injury can be positively influenced. Therapy positively affects the rate of healing, elimination of bacterial load and ultimately successful healing of the dermopeidermal graft
Discussion
Discussion of limb salvage or amputation is appropriate for such serious injuries. However salvaged limb does not guarantee functionality, normal life, a pain-free extremity or employability 9, 10
We think that the NPWT has made treatment relatively fast with minimal complications. Classical therapy for wound healing would take longer and be uncertain according to more risk of bacterial load and slow granulation of soft tissues.
This method is considered the method of choice in the treatment of severe limb injuries with soft tissue laceration. After successful therapy, limb function is another target in the treatment.
Conclusion
The great advantage of therapy is the acceleration of wound healing and overall shortening of the patient's treatment. Our case reports provide a view of treatment using vacuum therapy. Presented case report confirms the effectiveness and importance of therapy.
Treatment with NPWT shortens the length of hospitalization, lower the number of regular dressings, therefore, treatment is economically effective in a complex concept.
Recent experience has determined that this method is required for each trauma of this type.
Abbreviations
NPWT: negative presure wound therapy
V.A.C: vaccum assisted closure
ATB: antibiotics
G-A: Gustillo Anderson open fracture classification
125 mmHg: pressure 125 millimeters of hydrargyrum
Ethics
We received consent from the participants of the case report to the presentation.
References
- 1.Johansen K, Daines M, Howey T, Helfet D, Hansen Jr ST. (1990) Objective criteria accurately predict amputation following lower extremity trauma. , J Trauma 30, 568-73.
- 2.Morykwas M J, Argenta L C, Shelton-Brown E I, McGuirt W. (1997) Vaccum-Assisted Closure: a New Method for Wound Control and Treatment: Animal Studies and Basic Foundation.Ann Plast Surg,38. 6, 553-562.
- 3.Morykwas M J, Falter B J, Pearce D J, Argenta L C. (2001) . Effects of Varying Levels of Subatmospheric Pressure on the Rate of Granulation Tissue Formation in Experimental Wound in Swine.Ann Plast Surg.47(5): 547-551.
- 4.Argenta L C, Morykwas M J. (1997) Vaccum-Assisted Closure: a New Method for Wound Control and Treatment: Clinical Experience.Ann Plast Surg.38(6): 563-576, discussion 577.
- 5.Webb L X. (2002) New Techniques in Wound Management: Vaccum-Assisted Wound Closure.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.10(5):. 303-311.
- 6.Fabian T S, Kaufman H J, Lett E D. (2000) . The Evaluationof Subatmospheric Pressure and Hyperbaric Oxygen in Ischemic Full-Thickness Wound Healing.Am Surg.66(12): 1136-1143.
- 7.Genecov D G, Schneider A M, Morykwas M J, Parker D, White W L et al. (1998) . Controlled Subatmospheric Pressure Dressing Increases the Rate of Skin Graft Donor Site Reepithelialization.Ann Plast.40(3): 219-225.
- 8.Chen S-Z, Li J, Li X-Y, Xu L-S. (2005) Effects of Vacuum-Assisted Closure on Wound Microcirculation: an Experimental Study. , Asian J Surg Asian Surg Assoc 28(3), 211-217.
- 9.Fodor L, Sobec R, Sita-Alb L, Fodor M, Ciuce C. (2012) Mangled lower extremity: can we trust the amputation scores?. , Int J Burns Trauma 2(1), 51-8.