Efficacy of The Immunotargeting Therapeutic Antibody Trastuzumab in HER2-Positive Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Gastric cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in the world, usually diagnosed at an advanced stage. Despite the advances in specific anticancer agents' development, the survival rates remain modest, even in early stages. HER2 overexpression was identified on 15% - 20% of gastric cancer patients. Trastuzumab-based chemotherapy provides obvious efficacy improving outcomes of HER2 positive gastric cancer patients. We performed a meta-analysis to estimate the efficacy of the addition of trastuzumab over chemotherapy. We identified randomized controlled trials (RCTs) which compare the addition of trastuzumab therapy to chemotherapy alone reporting progression-free survival (PFS), time to progression (TTP), overall survival (OS), and/or response rates as our eligible trials. Night trials including 1101 patients were eligible for analysis. Trastuzumab therapeutic partners were cisplatin (9 RCTs), 5-fluorouracil (8 RCTs), capecitabine (6 RCTs), irinotecan (1 RCTs), docetaxel (1 RCTs), oxaliplatin (1 RCTs), and leucovorin (1 RCTs). The addition of trastuzumab agents improved OS (HR = 0.80; 95% CI = 0.72 - 0.89), PFS (HR = 0.70; 95% CI = 0.59 - 0.83), TTP (HR = 0.69; 95% CI = 0.57 - 0.83), and overall response rate (RR = 1.22; 95% CI = 0.94 - 1.59), DCR (RR = 1.19; 95% CI = 1.10 - 1.28). Our meta-analysis affirmed the efficacy of adding trastuzumab agent to chemotherapy in HER2 positive gastric cancer.
Author Contributions
Academic Editor: Zhanjun Jia, Children’s Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, China
Checked for plagiarism: Yes
Review by: Single-blind
Copyright © 2018 Yunxiao Yang, et al.
 This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Citation:
Introduction
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is involved in the pathogenesis and poor outcomes of several types of cancer, including advanced gastric cancer and gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma[1]. HER2 is a member of the HER family, encoded by proto-oncogene ERBB2 on chromosome 17, and consists of four plasma membrane-bound receptor tyrosine kinases which transmit extracellular signals to initiate cellular signaling pathways by phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT), phospholipase C (PLC) and protein kinase C (PKC)2. Trastuzumab, an immunetargeting therapeutic antibody monoclonal antibody directed against HER23. Over the last decade, trastuzumab has revolutionized the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer and improved its outcomes4. Based on these findings, trastuzumab is now considered a key drug for treating HER2-positive breast cancer. With increasing understanding of the molecular biology of HER2, and the availability of genomics and proteomics analyses, it has now been recognized that HER2 is also present in other cancers, particularly in gastric cancer 1, 5.
The backbone treatment of gastric cancer is cytotoxic chemotherapy. Regimens containing a fluoropyrimidine add a platinum component, and usually including epirubicin or docetaxel, or a fluoropyrimidine plus a platinum compound have been most widely used6, 7. However, patients with HER2-positive gastric cancer are failure of these standard treatments and have poorer outcomes than patients with HER2 negative gastric cancer. HER2 is over-expressed ranging from 6 to 29.5 % of gastric cancer1, 8. HER2 has been known as a novel therapies targets against HER2-positive of gastric cancer. Wang et al9. also show that HER2-positive expression was associated with male gender, intestinal type, and well/moderate cell differentiation on gastric cancer via a meta-analysis.
Consequently, many studies have evaluated the relationship between HER2 status and prognosis in patients with gastric cancer10, 11, 12. Unlike in breast cancer, the studies in gastric cancer to date have yielded inconsistent findings regarding the prognostic relevance of HER2. Some studies showed that HER2 positivity was associated with a significantly worse prognosis10, 11, whereas others found no association between HER2 status and prognosis12, 13, or that median overall survival was longer in HER2-positive than in HER2-negative patients12. Gu et al14. showed that HER2 expression based on ToGA criteria is not related to the survival in patients with gastric cancer. Therefore, the relationship between HER2 status and prognosis of gastric cancer patients remains controversial.
In this study, we performed a meta-analysis to estimate the efficacy of trastuzumab-based chemotherapy on HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer. The major endpoints used in clinical trials were overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), intermediate endpoints of time to progression (TTP), overall response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR). We try to find the best strategy for second-line treatment of HER2 positive gastric cancer.
Materials and Methods
Search Strategy
We identified trials by searching PubMed, Cochrane Library, Ebsco, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, and Chinese Biomedical databases (up until April 2017). No language restrictions applied. PubMed searched using ‘trastuzumab’ and the exploded MeSH term ‘gastric neoplasms’. We reviewed the trial registries of Clinical Trials.gov, National Cancer Institute Clinical Trials to ensure the included trials.
Selection Criteria
We selected phase II or III randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing the efficacy of trastuzumab-based chemotherapy in gastric cancer. We included trials of gastric cancer patients with HER2-positive status. We excluded trials if they compared only the outcomes of different HER2 treatment dosing scheme, only measurement toxic effects, quality of life, pharmacokinetic efficacy or without control and case-control experiment. Studies were excluded without sufficient published data for estimation of the odds ratio (OR), and 95% confidence interval (CI) as well.
Data Extraction
We extracted data strictly abide by Cochrane guidelines. Two reviewers (Huahui Li and Bihua Lin) evaluated independently the titles and abstracts of eligible publications to determine trial inclusion. Including design of trial, eligibility of patient, baseline characteristics of patient, dosing scheme, treatment line, HER2 identification method, follow-up duration and therapy changes on disease progression. Any disagreements between reviewers were resolved by a third researcher (Keyuan Zhou). If the test results repeat in various publications, we got the most complete endpoints.
We abstracted hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the endpoints OS, TTP and PFS. We also abstracted the endpoints of overall partial response (PR), complete response (CR), stable disease (SD), poresponse rate (ORR), progressive disease (PD), time to treatment failure (TTF), clinical benefit rates (CBR), and total of deaths. The data extract documented relevant items, involving the surname of author, year of publication, age of the participants, HER2 status, and sample number of trial.
Statistical Analysis
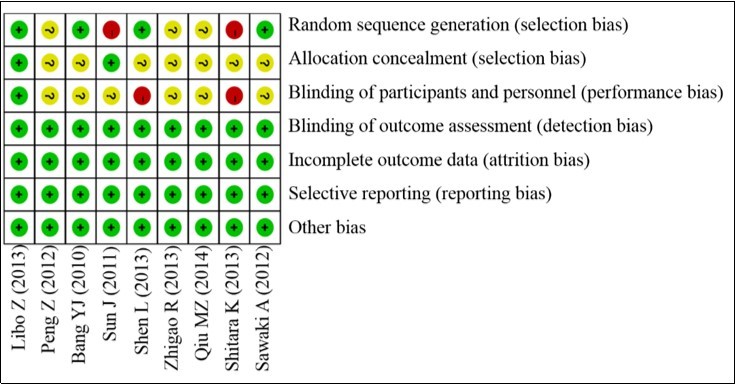
Log HRs and standard errors were calculated for OS, PFS, and TTP endpoint. Inverse-variance method was used for pooled the separate trial log HRs. Mantel–Haenszel method pool the rate-based secondary outcome15, 16. Based to Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2, heterogeneity with I2 <25% indicating low heterogeneity, 25 % <I2<50% indicating medium heterogeneity. Results with low heterogeneity were using fixed effects models; otherwise using random effects models. All studies were carry out using the Stata Version 12.0 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA), the publication bias evaluated by Begg’s test (P<0.05 was considered significant). Each study was assessed by risk assessment of Cochrane Collaboration tool. A grade was defined as high-quality, low risk of publication bias, or else they were considered as low-quality. The quality assessment analysis outlined in Figure 1.
Results
Search Results
We identified the titles and abstracts of 446 citations, 69 articles excluded. The full-text reports of 377 articles were took to further determine eligibility. Night manuscripts were included in the meta-analysis17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25. The night trials represented 1101 patients, 562 obtaining the trastuzumab and 536 receiving chemotherapy alone (Figure 2). If papers included both HER2 positive and negative patients, only HER2 patients were included in our meta-analysis18. Chemotherapy partners included capecitabine + cisplatin or 5-fluorouracil + cisplatin(5 trials)17, 19, 20, 21, 25, Docetaxel + cisplatin + 5-fluorouracil (2 trials)18, 23, Irinotecan + 5-fluorouracil/Leucovorin (1 trial)21, trastuzumab + capecitabine + oxaliplatin (1 trial). Overall, 4 studies were reported in English and 5 in Chinese. Trials were either first line or a second or subsequent line of therapy. The trials of HER2 positive disease was via identified immunohistochemistry (IHC) + or FISH+. We further analysis of these studies characteristic in Table 1.
Figure 2.Identification of eligible studies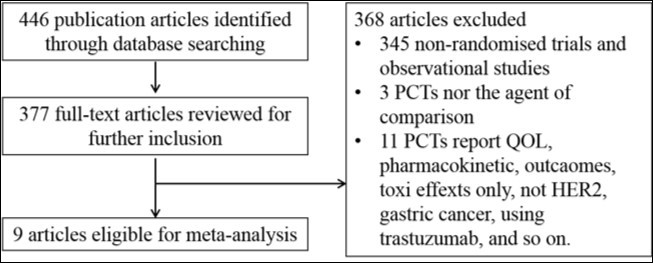
| Studies | Experimental group | Control group | Cycles of therapeutic partner | Line of treatment | median follow up (months) | HER2 status |
| Sawaki A (2012) | Trastuzumab + Capecitabine / Cisplatin or 5- FU / Cisplatin (n = 51, Median age = 63 years) | (Capecitabine + Cisplatin or 5- FU + Cisplatin) (n = 50, Median age = 63.5 years) | 8 | Second | 18.6 | IHC3+, IHC0/1+, IHC2+FISH+ |
| Shitara K (2013) | Trastuzumab + Chemotherapy (n = 43) | Chemotherapy (n = 415) | Until progression | First or second | 38.9 | IHC2+IHC3+ |
| Qiu MZ (2014) | Trastuzumab + Chemotherapy (n = 51, Median age = 57 years) | Chemotherapy (n = 47, Median age = 59 years) | 4 | First | 13.5 | IHC2+ |
| Bang YJ (2010) | Trastuzumab + Chemotherapy (n = 298, Median age = 59.4 years) | (Capecitabine + Cisplatin or 5- FU + Cisplatin) (n = 294, Median age = 58.5 years) | 6 | First | 18.6 | IHC3+,IHC0/1+, IHC2+FISH+ |
| Shen L (2013) | Capecitabine or 5-FU plus Cisplatin + Trastuzumab (n = 36, Median age = 58.7 years) | Capecitabine or 5-FU plus Cisplatin (n = 48, Median age = 58.2 years) | 6 | First or second | 36 | IHC+ FISH+ |
| Sun J (2011) | Trastuzumab + Irinotecan plus 5-FU/LV (n = 17, Median age = 56.1 years) | Irinotecan plus 5-FU/LV (n = 17, Median age = 56.5 years) | 2 - 4 | Not stated | Not stated | IHC+ |
| Libo Z (2013) | Trastuzumab + Docetaxel + Cisplatin + 5- FU (n = 37, Median age = 56.8 years) | Docetaxel + Cisplatin + 5- FU (n = 35, Median age = 56.3 years) | 4 | Not stated | Not stated | FISH+ |
| Peng Z (2012) | Trastuzumab + DDP + Xeloda (n = 14, Median age = 55.1 years) | Capecitabine +Cisplatin (n = 16, Median age = 58.8 years) | 6 | Not stated | Not stated | IHC+ |
| Zhigao R (2013) | Trastuzumab + Capecitabine +Oxaliplatin (n = 18) | Capecitabine + Oxaliplatin (n = 14) | 4 - 6 | Not stated | Not stated | FISH+ |
Meta-Analysis
Our meta-analysis exhibited a 20% decrease in the hazard of death with the trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy to chemotherapy alone (5 trials, 933 patients, HR = 0.80; 95% CI = 0.72 - 0.89) (Figure 3). The benefit of trastuzumab over chemotherapy alone was also seen with the endpoints of PFS (HR = 0.70; 95% CI = 0.59 - 0.83) and TTP (HR = 0.69; 95% CI = 0.57 - 0.83) and pooled results for outcomes (Figures 3). The addition of trastuzumab therapy to chemotherapy treatment have an insignificance ORR (Relative risk (RR) = 1.22; 95% CI = 0.94 - 1.59) (Figure 4). The addition of trastuzumab also was beneficial for the outcomes of partial response (RR = 1.26, 95% CI = 0.99 - 1.59). Disease control rate (complete remission + partial response + Stable disease) demonstrated a 19% increase in the relative risk (6 trials, 942 patients, RR = 1.19; 95% CI = 1.10 - 1.28) (Figure 5). The incidence of adverse events was similar in the control and trial arms of the addition of trastuzumab therapy. A difference was only observed with increased in grade 3~4 adverse reactions in patients with diarrhea in the trial arms (4 trials, 875 patients, RR = 2.40; 95% CI = 1.34–4.32) (Figure 6). Testing publication bias by endpoint parameters showed no evident asymmetry in the funnel plots by the Egger’s test (P > 0.05).
Figure 3.The OS, PFS and TTP for trastuzumab-based chemotherapy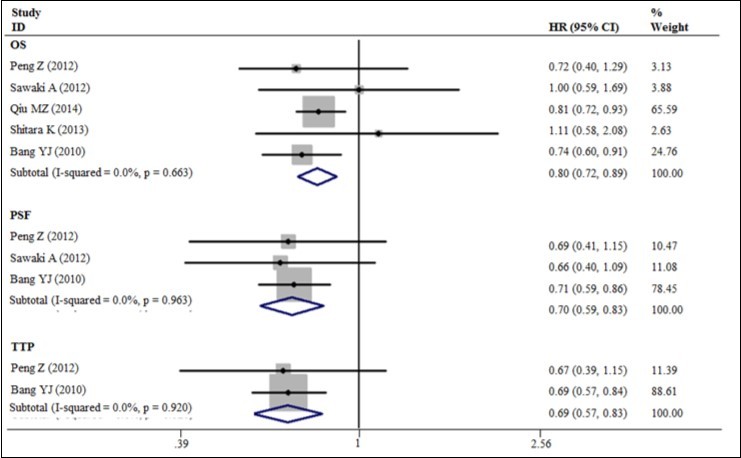
Figure 4.The overall response rates for trastuzumab-based chemotherapy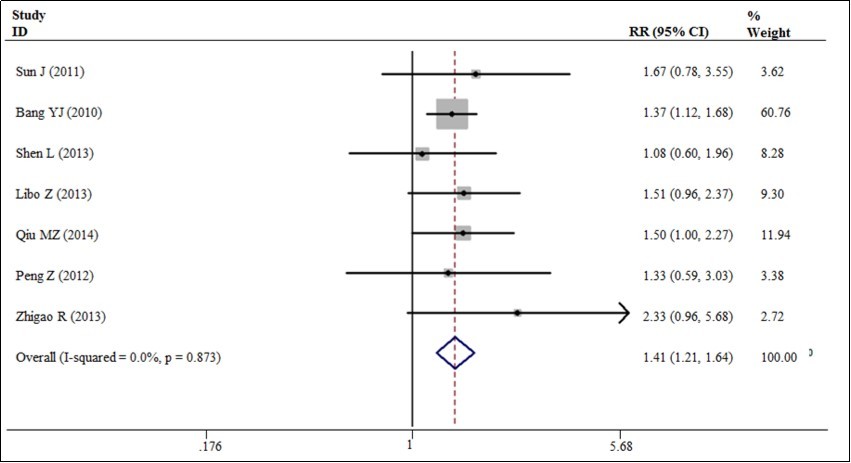
Figure 5.Disease control rate for trastuzumab-based chemotherapy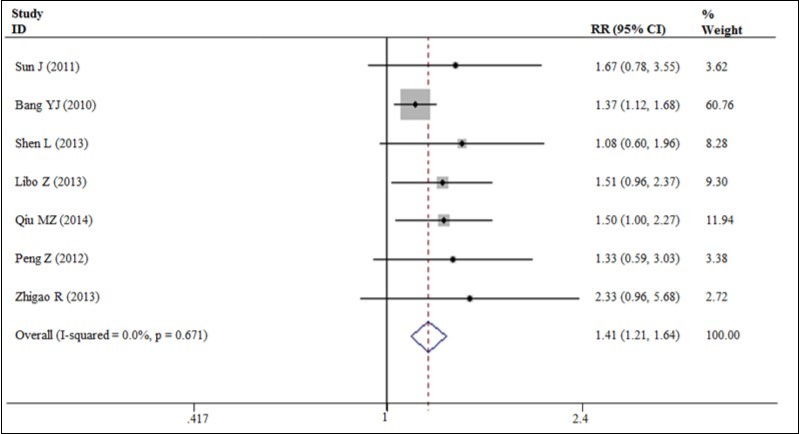
Figure 6.Disease control rate for trastuzumab-based chemotherapy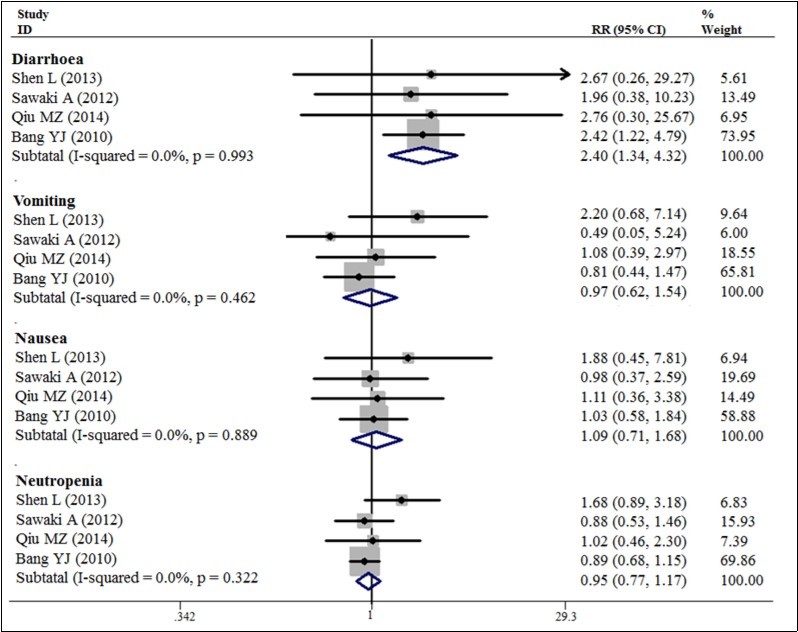
Sensitivity Analysis
Oursensitivity analysis was executed by successively eliminating studies one by one. The elimination of one study each time revealed no significant difference in whole estimates, suggesting the stabilization of these results.
Discussion
Our pooled results of 9 studies show that the addition of trastuzumab therapies to chemotherapy provides a 20% improvement in OS. PFS and TTP show a 30% and 31% improvement, respectively, and significance increase in ORR of 41%. The pooled results improve some of the uncertainties about the benefit of trastuzumab therapies. Some trials included only small patients don’t report on the endpoint of OS, PFS or TTP. A few HER2 combination therapies have been evaluated in a randomized controlled trials design, specifically capecitabine, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, irinotecan, docetaxel, Leucovorin and oxaliplatin). It may be helpful to carry out further clinical trials to compare the efficacy of trastuzumab therapy over chemotherapy. The clinical evidence suggest that trastuzumab therapy could be continued on patients with HER2-positive gastric cancer, even in patients who need to discontinue chemotherapy because of adverse reactions. Additionally, more data are still needed to confirm whether trastuzumab should be continued after disease progression. The introduction of trastuzumab led to the establishment of a new disease entity, “HER2-positive gastric cancer,” similar to HER2-positive breast cancer. It is expected that more and more anti-HER2 drugs should be developed and introduced into clinical practice to treat patients with HER2-positive gastric cancer.
Due to the various therapeutic scheme and small sample of trials, we can’t undertake a subgroup analysis of individual therapeutic scheme. This study also has a lot of limitations, some of which are approach in meta-analysis and others detailed to our analysis. We don’t have personal patient data in order to confirm outcomes data showed in publications. Moreover, we are incapable to confirm blinding procedures or randomization26. In addition, the current included trials are lack of long-term follow-up data. These limitations in clinical practice call for building an unbiased and current evidence to support the best use of trastuzumab therapies. Reporting diverse greatly in the included trials such as the endpoints are used and the way are expressed. The endpoints HRs and CIs included in our study are not always reported in every trial. However, many trials report the period of advantage in days, weeks or months. We try to fill some of the gaps by contacting individual researchers, but we fail to obtain additional data.
The results of this study show that trastuzumab-based chemotherapy can significantly improve overall survival in patients with HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer, compared with chemotherapy alone, and this improvement is particularly significant in patients with high HER2 expression. It is also notable that trastuzumab don’t increase the incidence of adverse events that associated with chemotherapy and that the rate of cardiac events is also low. Therefore, These studies should support an indication for trastuzumab as part of a perioperative chemotherapeutic regimen for treating HER2-positive gastric cancer.
In conclusion, this study provides obvious efficacy of trastuzumab-based chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in gastric cancer, in terms of OS, PFS, TTP, RR and DCR endpoints. Trastuzumab-based chemotherapy increased grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions in patients with diarrhea, but there is not enough evidence that will add other adverse reactions in patients. A well-designed RCTs should establish to determine the ideal therapeutic scheme for trastuzumab therapies.
Acknowledgements
Funding
This study was supported by the Medical Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (A2015206, A2016278 and A2016395), the Science and Technology Project of Dongguan (2016105101292, 2016108101030 and 201750715005451), the National and Guangdong Provincial College Students' innovative Entrepreneurial Training Program (201710571009, 201710571033), and the College Students' innovative experiment projects of Guangdong Medical University (Z2016005, GDMU2016009 and GDMU2016033).
References
- 1.Abrahao-Machado L F, Scapulatempo-Neto C. (2016) HER2 testing in gastric cancer: An update. , World J Gastroenterol 22(19), 4619-25.
- 2.Dittrich A, Gautrey H, Browell D. (2014) The HER2 Signaling Network in Breast Cancer--Like a Spider in its Web. , J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia.19(3-4): 253-70.
- 3.Wong W M. (1999) Drug update: trastuzumab: anti-HER2 antibody for treatment of metastatic breast cancer. , Cancer Pract 7(1), 48-50.
- 4.Maly J J, Macrae E R. (2014) Pertuzumab in Combination with Trastuzumab and Chemotherapy in the Treatment of HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: Safety, Efficacy, and Progression Free Survival. , Breast Cancer (Auckl) 8, 81-8.
- 5.Curea F G, Hebbar M, Ilie S M. (2017) Current Targeted Therapies in HER2-Positive Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 32(10), 351-363.
- 6.Kang Y K, Kang W K, Shin D B. (2009) Capecitabine/cisplatin versus 5-fluorouracil/cisplatin as first-line therapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer: a randomised phase III noninferiority trial. , Ann Oncol 20(4), 666-73.
- 7.Koizumi W, Narahara H, Hara T. (2008) S-1 plus cisplatin versus S-1 alone for first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer (SPIRITS trial): a phase III trial. , Lancet Oncol 9(3), 215-21.
- 8.Kurokawa Y, Matsuura N, Kimura Y. (2015) Multicenter large-scale study of prognostic impact of HER2 expression in patients with resectable gastric cancer. , Gastric Cancer 18(4), 691-7.
- 9.Wang H B, Liao X F, Zhang J. (2017) Clinicopathological factors associated with HER2-positive gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. , Medicine (Baltimore) 96(44), 8437.
- 10.Dang H Z, Yu Y, Jiao S C. (2012) Prognosis of HER2 over-expressing gastric cancer patients with liver metastasis. , World J Gastroenterol 18(19), 2402-7.
- 11.Otsu H, Oki E, Ikawa-Yoshida A. (2015) Correlation of HER2 expression with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis in resectable gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 35(4), 2441-6.
- 12.Janjigian Y, Werner D, Pauligk C. (2012) Prognosis of metastatic gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer by HER2 status: a European and USA International collaborative analysis. , Ann Oncol 23(10), 2656-62.
- 13.Shen G S, Zhao J D, Zhao J H. (2016) Association of HER2 status with prognosis in gastric cancer patients undergoing R0 resection: A large-scale multicenter study in China. , World J Gastroenterol 22(23), 5406-14.
- 14.Gu J, Zheng L, Wang Y. (2014) Prognostic significance of HER2 expression based on trastuzumab for gastric cancer (ToGA) criteria in gastric cancer: an updated meta-analysis. , Tumour Biol 35(6), 5315-21.
- 15.Tierney J F, Stewart L A, Ghersi D. (2007) Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. , Trials 8, 16.
- 16.Wang Y, Zeng T. (2013) Response to:Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. , Trials 14, 391.
- 17.Sawaki A, Ohashi Y, Omuro Y. (2012) Efficacy of trastuzumab in Japanese patients with HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a subgroup analysis of the Trastuzumab for Gastric Cancer (ToGA) study. , Gastric Cancer 15(3), 313-22.
- 18.Shitara K, Yatabe Y, Matsuo K. (2013) Prognosis of patients with advanced gastric cancer by HER2 status and trastuzumab treatment. , Gastric Cancer 16(2), 261-7.
- 19.Qiu M Z, Li Q, Wang Z Q. (2014) HER2-positive patients receiving trastuzumab treatment have a comparable prognosis with HER2-negative advanced gastric cancer patients: a prospective cohort observation. , Int J Cancer 134(10), 2468-77.
- 20.Bang Y J, E Van Cutsem, Feyereislova A. (2010) Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. , Lancet 376(9742), 687-97.
- 21.Sun J, Pan S Y, Chen Q Q. (2013) Efficacy of trsatuzumab (Herceptin) combined with FOLFIRI regimen in the treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 31(8), 1458-60.
- 22.Shen L, Xu J M, Feng F Y.Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for first-line treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a Phase III, multi-center, randomized controlled trial, Chinese subreport. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 35(4), 295-300.
- 23.Libo Z, Xing L, Linlin L. (2013) Clinical Effect and Two-year's Prognosis of Herceptin Combined with Conventional Chemotherapy. in Treatment of Advanced Cardiac Carcinoma Patients with HER-2 Over Expression. Progress in Modern Biomedicine 10(1), 67-70.
- 24.Zhigao R, Youhui W, Hanjie Y. (2013) Transtuzumab combined with capecitabine and oxalipatin in treatment of advanced gastric cancer. , Zhejiang Medical Journal 35(21), 1906-1910.