Morphological Variations and Morphometric Analysis of Foramen Ovale in South Indian Population
Abstract
Introduction
The foramen ovale is located in the area where intracranial and extracranial structures meet. Procedures involving trigeminal neuralgia and mandibular nerve anaesthesia require an understanding of the foramen ovale's morphometry and anatomy. Our present study was conducted to define mean values and anatomical variations in foramen ovale.
Aims
1. To establish the mean length, breadth and the Area of the foramen ovale. 2. And also to study different shapes and special features of the foramen ovale. 3. To compare the values of the present author with the previous studies.
Methodology
The study was carried out on100 foramen ovale using 50 dry adult human skull bones of unknown sex. Maximum transverse diameter, antero-posterior diameters of the foramen were measured with the help of vernier calipers. and the different shapes of foramen were noted. The data was analysed by using unpaired T test.
Results
The mean anteroposterior diameter on left side was 6.59±1.37 mm and on right side was 6.99±1.44 mm. The mean transverse diameter on the left is 4.09±0.74 mm and 4.17±0.76 mm on the right side. Incidences of various shapes of the foramen ovale were oval 70%, almond 11%, round 9%, elongated 6%, pear shaped 2 % and irregular 2%.
Conclusions
The findings from the current study may be useful for understanding the variations of these foramina for interventions in middle cranial fossa.
Author Contributions
Academic Editor: Abdelmonem Awad Mustafa Hegazy, Professor and Former Chairman of Anatomy and Embryology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt.
Checked for plagiarism: Yes
Review by: Single-blind
Copyright © 2024 Supriya Garapati, et al
 This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Citation:
Introduction
Foramen ovale is present medial to the foramen spinosum and foramen lacerum is located medial to the foramen ovale. It transmits the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve, accessory meningeal branch of the maxillary artery, lesser petrosal nerve and an emissary vein which connects the pterygoid venous plexus in the infratemporal fossa to the cavernous sinus 1.
The foramen ovale is located in the area where intracranial and extracranial structures meet 2. Procedures involving Trigeminal Neuralgia and mandibular nerve anaesthesia require an understanding of the foramen ovale's morphometry and anatomy 3. Foramen Ovale is also used for patients undergoing selective amygdalohippocampectomy, percutaneous biopsy of cavernous sinus tumours, and micro vascular decompression by percutaneous trigeminal rhizotomy for trigeminal neuralgia to analyse electroencephalographic seizure data. Hence it is used for diagnostic and surgical procedures 4.
Our present study was conducted to define mean values and anatomical variations in foramen ovale. This work intends to highlight such prior knowledge of changes in foramen ovale, which may be useful for forensic, anthropological, and surgical purposes.
Methodology
The retrospective cross-sectional study was carried out on100 foramen ovale using 50 dry adult human skull bones of unknown sex, the bones were taken from department of Anatomy, AIIMS Bibinagar Hyderabad. Skulls which were fractured at the surroundings of foramen ovale were excluded from the study.
a) Maximum transverse diameter, antero-posterior diameters of the foramen were measured with the help of vernier calipers (Carbon Fiber Composites Digital Caliper(RoHS)) ( Picture 1& Picture 2)
Picture 1.Measurement of vertical length
Picture 2.Measurement of Horizontal length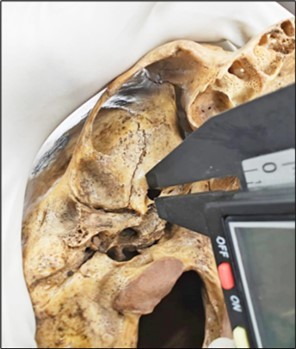
b) Different shapes of foramen were noted. (Picture 3)
Picture 3.Showing different shapes of Foramen Ovale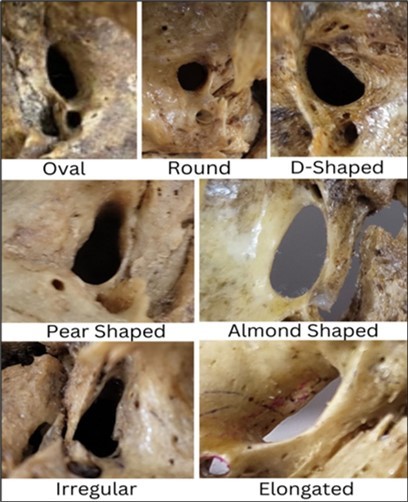
c) Margins of foramen were carefully observed for any bony projections.
d) The area of foramen ovale is calculated by using the formula 𝝿 x Length x Breadth/4 5
e) Unpaired t’ test was used for statistical analysis.
Results
Out of 100 foramen ovale, minimum to maximum anteroposterior diameter on left side were 3.9 mm 10 mm and on right side were 4.25 mm and 10.5 mm. The mean anteroposterior diameter on left side was 6.59±1.37 mm and on right side was 6.99±1.44mm. (Table 1)
Minimum transverse diameter on left side was 2.03mm and on right side was 2.45mm. Maximum transverse diameter was 6.16mm and 6.3mm on left and right sides respectively. The mean transverse diameter on the left is 4.09±0.74 mm and 4.17±0.76 mm on the right side. The mean area of the foramen ovale is 23.03+6.73 mm2 and 21.42+6.52 mm2 on the right and left sides respectively as shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Table showing the values of present author| REGION | DIMENTION | SIDE | MEAN+/- SD (mm) | RANGE (mm) | P VALUE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foramen Ovale | Length(mm) (AP Diameter) | Right | 6.99+/-1.44 | 4.25 – 10.5 | 0.160 |
| Left | 6.59+/-1.37 | 3.9 - 10 | |||
| Foramen Ovale | Width(mm) (Transverse diameter) | Right | 4.173+/-0.766 | 2.45 – 6.3 | 0.612 |
| Left | 4.096+/-0.743 | 2.03 – 6.16 | |||
| Foramen Ovale | Area (Square meter) | Right | 23.03 +/-6.73 | 0.227 | |
| Left | 21.42+/-6.52 |
Majority of the foramen were oval shaped and it was seen in 70 sides (left 36, right 34), almond shape was seen in 11 sides (4 left, 7 right), round shape was seen in 9 sides (6 left, 3right), pear shaped foramen was observed in 2 sides one on each side. 6 elongated shaped foramina (2 left and 4 right) were noted along with 2 irregular shaped foramina (1 left and 1 right) as shown in picture 3.
Incidences of various shapes of the foramen ovale ( Fig:1)were oval 70%, almond 11%, round 9%, elongated 6%, pear shaped 2 % and irregular 2%.
Discussion
The ossification of the base of the skull happens round existing arteries and cranial nerves, creating the skull foramina. The growth of cartilage around the already evident arteries and nerves starts after the eighth week of gestation.The greater sphenoidal wing's cartilaginous ossification starts from the 15th gestational week and lasts until the 22nd week, during which the foramen ovale develops.6, 7
The morphometric and developmental aspects of the foramen ovale have been the subject of a number of studies around the world. In our study, the mean anteroposterior diameter (length) on the left side was 6.59±1.37 mm and on the right side was 6.99±1.44mm; there is no statistically significant difference between the right and left side as shown in Table 1.. A similar study done in Japan demonstrated that the foramen ovale has an average maximum length of 7.48 mm and an average minimum length of 4.17 mm 8. In New York, laser targeting of the foramen ovale with the aid of fluoroscopy revealed mean lengths of 6.9mm on the right side and 6.8mm on the left 9. These studies have reported lower values when compared to our study where the maximum length on the right and left sides 10.5 mm and 10 mm respectively. Our study is similar to other Indian studies done by Patil et al., and Prakash et al., who documented that maximum length of foramen ovale was 9.5mm and 12.1 mm 10, 11. Another German study postulated that the foramen ovale in an adult's skull measures 7.2 mm in length and 3.7 mm in breadth 12. None of these studies have documented any significant statistical difference between the right and left sides. A radiological study done by Bhattarai et al., the mean length of foramen ovale to be 7.79±1.10 mm 13.
The maximum transverse diameter in our study was 6.16mm and 6.3mm on left and right sides respectively (Table 1) This is lower when compared to another Indian study where the maximum width of the foramen ovale was found to be 8.8 mm 10. On the contrary to our study, a radiological study documented the width of the foramen ovale to be lower than our findings which is only about 3.68±0.64 mm 13. Another Indian study documented that the the maximum and minimum length of foramen ovale on the right and left was 10.1 mm, 4.3 mm and 9.1 mm, 3.2 mm. On the contrary, a study in the New York population documented the foramen ovale's average width to be 3.4 mm on the right side and 3.8 mm on the left side 9. None of these studies have documented any significant statistical difference between the right and left sides. However, Berge et al., Shapiro et al., in their studies postulated that right sided foramen ovale is narrower than the left sided foramen ovale in most of the people 15, 16. Studies have shown that a small foramen ovale has been linked to primary trigeminal neuralgia relapse 17, 18, 19. Classical trigeminal neuralfia may be ascribed to the trigeminal nerve compressed by blood vessels and a narrow foramen ovale meanwhile. The mandibular nerve may enlarge as a result of neurovascular compression, which causes compression from a narrow foramen ovale and makes the nerve vulnerable to entrapment during its passage through a small foramen 20, 21. The mean area of the foramen ovale in our study is 23.03+6.73 mm2 and 21.42+6.52 mm2 on the right and left sides respectively. Bhattari et al., reported the mean area of foramen ovale to be 22.80±6.18 mm2 which is similar to our findings 13. On the contrary, Prakash et al., documented higher mean area of foramen ovale which is around 30.808 ± 7.545 mm2 and 31.310 ± 8.262 mm2 on the right and left respectively 14. The presence of increased length, width and area of the foramen ovale could be attributed also to more number of emissary veins passing through it 22.
In our study, as shown in picture 3, majority of the foramen were oval shaped and it was seen in 70 sides (left 36, right 34), almond shape was seen in 11 sides (4 left, 7 right), round shape was seen in 9 sides (6 left, 3right),pear shaped foramen was observed in 2 sides one on each side. 6 elongated shaped foramina (2 left and 4 right) were noted along with 2 irregular shaped foramina (1 left and 1 right) (picture 3). Similar other studies have also documented that oval shaped foramina are predominantly noted followed by almond shaped and round shaped foramina 14, 23, 24, 25, 26. Developmental factors lead to variations in foramen ovale forms, which can substantially impair clinical and diagnostic processes. Even though the foramen ovale's shape might vary in a healthy state, a careful examination of these foramina can help to diagnose abnormalities in the middle cerebral fossa and nasopharynx. It is tempting to think of a fifth nerve neurinoma when the foramen ovale enlarges 26. The authors also compared the values of present author with the previous studies. The comparison is represented in Table 2. There is a lot of variation among the parameters of different authors. The values of present author are more or less equal with Karishma et al 14
Table 2. Comparative table showing the values of parameters by different authors| S.No | Authors | Length of the foramen ovale (Anteroposterior diameter) | Width of the foramen ovale (Transverse diameter) | Area of the foramen ovale |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yanagi S etal., 8 | 7.48 mm | 4.17 mm | - |
| 2 | Landl MK et al., 9 | right side -6.9mm left side - 6.8mm | right side - 3.4mm left side - 3.8mm | - |
| 3 | Patil et al., 10 | right side -7.0±2.17mm left side- 6.8±1.40mm | right side - 5.0±0.42mm left side - 4.70±0.91mm | - |
| 4 | Prakash et al., 11 | Right – 7.64 ± 1.194 mmLeft – 7.561 ± 1.123 mm | Right – 5.128 ± 0.827 mmLeft – 5.244 ± 0.950 mm | Right - 30.808 ± 7.545 mm2Left - 31.310 ± 8.262 mm2 |
| 5 | Lang J et al., 12 | 7.2 mm | 3.7 mm | - |
| 6 | Karishma et al., 14 | right side- 6.773± 1.652 mmleft side- 5.744±1.791 mm | right side - 3.56±0.737mm left side- 4.28±0.833 mm. | - |
| 7 | Bhattarai et al., 13 | 7.79±1.10 mm | 3.68±0.64 mm | 22.80±6.18 mm2 |
| 8 | Present study | Right - 6.99±1.44mmLeft - 6.59±1.37 mm | Right - 4.17±0.76 mm Left - 4.09±0.74 mm | Right - 23.03+6.73 mm2Left - 21.42+6.52 mm2 |
Conclusion
These results can serve as a principal reference for future studies on FO morphological variation and its clinical applications. When conducting different diagnostic and surgical operations through the foramen ovale, neurosurgeons will find great utility in the differences seen in this study as well as the information regarding its location and dimensions.
References
- 1.Poornima B, Sampada P K, Mallikarjun M, Santosh B S. (2017) Morphometric and morphological study of foramen ovale in dry adult human skull bones. , Indian J. Clin. Anat. Physiol 4, 59-62.
- 3.Abd Latiff A, Das S, Sulaiman I M, KPP Hlaing, Suhaimi F H et al. (2009) The accessory foramen ovale of the skull: an osteological study. Clin Ter. 160(4), 291-3.
- 4.Wieser H G, Siegel A M. (1991) Analysis of foramen ovale electrode-recorded seizures and correlation with outcome following amygdalohippocampectomy. Epilepsia. 32(6), 838-50.
- 5.Bokhari Z H, Munira M, Samee S M, Tafweez R. (2017) A morphometric study of foramen ovale in dried human skulls. 11(16), 61-5.
- 6.W R Nemzek, H A Brodie, S T Hecht, B W Chong, C J Babcook et al. (2000) plain film imaging of the developing skull base in fetal specimens. , AJNR Am 21(9), 99-706.
- 7.Padget D H. (1956) The cranial venous system in man in reference to development, adult configuration, and relation to the arteries. , Am 98(3), 307-55.
- 8.Yanagi S. (1987) [Developmental studies on the foramen rotundum, foramen ovale and foramen spinosum of the human sphenoid bone]. Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi. 62(3), 485-96.
- 9.Landl M K, Grand Walter. (2005) Trigeminal Neuralgia: Fluoroscopically –Assisted Laser Targeting of the Foramen Ovale: Technical Note. Minrad International Inc.
- 10.Patil J, Kumar N, K G MR, S, S N et al. (2013) The Foramen Ovale Morphometry of Sphenoid Bone in South Indian Population. J Clin Diagn Res JCDR. 7(12), 2668-70.
- 11.Prakash K G, Saniya K, Honnegowda T M, Ramkishore H S, Nautiyal A. (2019) Morphometric and Anatomic Variations of Foramen Ovale in Human Skull and Its Clinical Importance. Asian. 14(4), 1134-7.
- 12.Lang J, Maier R, Schafhauser O. (1984) [Postnatal enlargement of the foramina rotundum, ovale et spinosum and their topographical changes]. Anat Anz. 156(5), 351-87.
- 13.Bhattarai R, Panthi S, Yadav G K, Bhandari S, Acharya R et al. (2023) Morphometric analysis of foramen ovale, foramen spinosum, and foramen rotundum of human skull using computed tomography scan: a cross-sectional study. Ann Med Surg. 85(5), 1731-6.
- 14.Karishma R. (2015) ThenmozhiMorphometric Study of Size and Symmetry of Foramen Ovale in Dry Skulls. , J. Pharm. Sci. & Res 7(10), 830-833.
- 15.Berge J K, Bergman R A. (2001) Variations in size and in symmetry of foramina of the human skull. , Clin Anat N Y 14(6), 406-13.
- 16.Shapiro R, Robinson F. (1967) The foramina of the middle fossa: a phylogenetic, anatomic and pathologic study. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 101(4), 779-94.
- 17.Li S, Liao C, Qian M, Yang X, Zhang W. (2022) Narrow ovale foramina may be involved in the development of primary trigeminal neuralgia. Frontiers in Neurology. 11, 1013216.
- 18.Iwanaga J, Clifton W, Dallapiazza R F, Miyamoto Y, Komune N et al. (2020) The pterygospinous and pterygoalar ligaments and their relationship to the mandibular nerve: Application to a better understanding of various forms of trigeminal neuralgia. Ann Anat. 229, 151466-10.
- 19.Rao B S, Yesender M, BHS Vinila. (2017) Morphological variations and morphometric analysis of foramen ovale with its clinical implications. , Int J Anat Res 5, 3394-7.
- 20.Love S. (2001) Coakham HB. Trigeminal neuralgia: pathology and pathogenesis. , Brain 124(12), 2347-60.
- 21.Hilton D A, Love S, Gradidge T, Coakham H B. (1994) Pathological findings associated with trigeminal neuralgia caused by vascular compression. , Neurosurgery 35(2), 299-303.
- 22.Henderson W R. (1966) A note on the relationship of the human maxillary nerve to the cavernous sinus and to an emissary sinus passing through the foramen ovale. J Anat. 100(4), 905-8.
- 23.Kaur A, Singla R, Sharma R. (2022) An Anatomical Evaluation of Normal and Aberrant Foramen Ovale. in Skull Base with Its Clinical Significance. Mædica 17(2), 357-62.
- 24.Sophia M M, Shruthy K M, Sasirekha M. (2018) A morphometric study on foramen ovale. , Int J Anat Res 6, 5915-5920.
- 25.Murugan M, Saheb S H.Morphometric and morphological study of foramen ovale. , Int J Anat Res 2014, 664-667.