Solitary Splenic Hydatid Cyst
Abstract
Splenic hydatid cyst is very rare, caused by the parasite echinococcus granulosus. Humans are considered an accidental intermediate host in the development of the parasite cycle. It poses a diagnostic dilemma with other cystic masses despite improved medical imaging techniques often requiring exploratory surgeries for fear of missing out on a malignant tumor. Total or partial splenectomy remains the treatment of first choice and the most effective. We report a case of solitary splenic hydatid cyst and discuss the different differential diagnoses and therapeutic modalities.
Author Contributions
Academic Editor: Qiping Dong, China.
Checked for plagiarism: Yes
Review by: Single-blind
Copyright © 2021 Zakaria MERAD
 This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Citation:
Introduction
Splenic hydatid cyst is a parasitosis caused by the development of the larvae of echinococcosis granulosis, it is very rare with annual incidence between 0.5% and 4%. 1, 2 Humans are an accidental intermediate host and become infected by eating raw food contaminated by the parasite 3. The hydatid cyst is usually discovered incidentally by a mass in the left hypochondrium, sometimes with complications such as constipation, dyspnea or even dysphagia4. The mechanism of splenic involvement is poorly understood, probably via the arterial route 5. The treatment is surgical without forgetting to take precautions to avoid the dissemination of scolices 6.
Case Report
It was a 50-year-old man, living in the companion with the notion of contact with animals, especially sheep, with no particular history admitted to the emergency for malaise associated with a deterioration of the general condition with nausea and vomiting (weight 45 kg). On admission, the patient was afebrile (36.8 °), eupneic (23 cycles / min, 95% oxygen saturation), tachycardium at 120 beats / min with a blood pressure of 130/85. His wife mentioned that the mass had started to overgrow over the last seven months. Physical examination found abdominal asymmetry and a mass in the left hypochondrium. Abdominal ultrasound revealed a thin-walled, unilocular cystic formation with calcification, occupying almost the entire spleen, measuring 12 cm in the antero-posterior axis. The biological assessment showed hypereosinophilia. The hydatid serology (direct haemagglutination) was positive (1/300). The abdominal scanner revealed a fluid collection occupying the entire spleen, the wall of which was discreetly enhanced after injection of contrast product measured 15cm / 12cm. There was no involvement of liver or other organs. A total splenectomy was performed urgently for the compression of neighboring organs. Macroscopic study found a part of total splenectomy measuring 20 / 15cm (figure 1) with at the opening the presence of a cystic formation occupying the entire spleen containing whitish membranes and numerous vesicles (figure 2) and the histological examination concluded to a hydatid splenic cyst. The postoperative course was straightforward and the patient was discharged on the eighth day with medical treatment based on albendazole for three months.
Figure 1.Macroscopic appearance of a splenic hydatid cyst.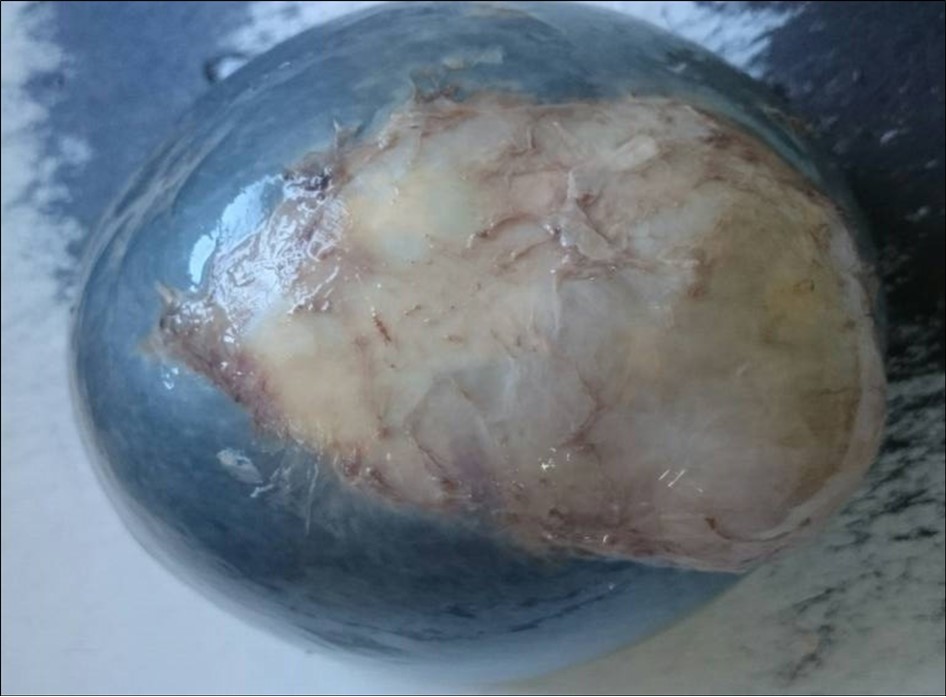
Figure 2.Shows cut section macroscopic of splenic hydatid cyst in centre there is hydatid membranes white.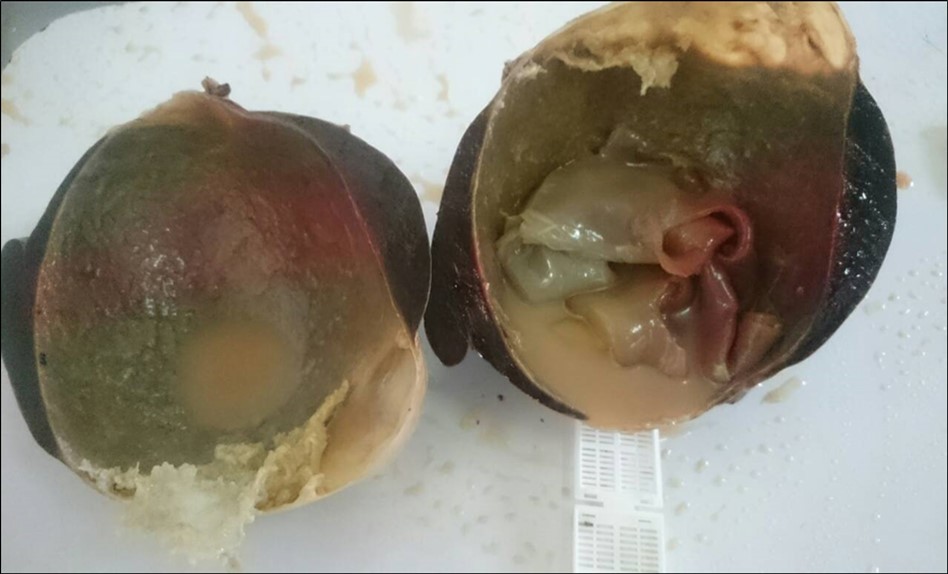
Discussion
The hydatid cyst (echinococcus granulosus) constitutes a major public health problem in endemic regions especially Africa, Asis, Latin America and Australia where their main activities are cattle breeding. Splenic hydatid cyst is very rare with an annual incidence between 0.5% and 4% 1, 2. The most common sites of hydatid disease are the liver (60–70%), which acts as a first filter and the lungs (10–40%), which acts assecond filter. The rare sites include spleen, thyroid, gall bladder, central nervous system, kidney, psoas sheet, retroperitoneal region, orbit. Practically any organ can be infested by hydatid disease 4.
The parasite's life cycle requires two hosts, the fox or dog which is the major definitive host and the rodents which are intermediate hosts. Man is an accidental intermediate host, becomes contaminated by eating raw vegetables contaminated by the faeces of infected carnivores or directly by touching these animals and this is the occasion of immunosuppression following an inflammatory or viral or bacterial disease. that hydatid disease is discovered 3, 4.
The mechanism of splenic involvement is poorly understood. Arterial dissemination of an echinococcosis granulosus embryo that has passed hepatic and pulmonary filters seems the most likely theory 5.
Berlot is the first to describe the splenic hydatid cyst discovered on autopsy in 1790 4 therefore the circumstances of discovery are variable and depend on the evolutionary stage of the disease, echinococcosis granulosus can be manifested by atypical pain in the left hypochondrium and nonspecific, low back pain or by a palpable mass, sometimes complications such as tachycardia, dyspnea, deterioration of the general condition (in our case) or even dysphagia when the volume of the cyst is large 6.
In practice, the biological examinations are normal except for a slight eosinophilia, the serological tests proposed for the diagnosis of echinococcosis granulosus are first, the sensitive Elisa test, if it is positive, it must be followed by a another test that of Western-Bloot to confirm the diagnosis 7, 8.
Ultrasound and computed tomography CT play an important role in the diagnosis of echinococcosis granulosus allowing to better specify the site and the relationships with neighboring organs, the most frequently found appearance is that of a cystic mass with a wall thin with sometimes an appearance of detachment of membranes or the presence of daughter vesicles 4, 5, 6.
Splenic hydatid cyst poses a diagnostic dilemma for clinicians with many pathologies such as angiosarcoma in its cystic form, lymphangioma, epidermal cyst and dermaid 2, 3, 6, 8, 9. The main complication is the rupture of the cyst leading to death from anaphylactic shock 1, 4, 6, 10.
The puncture aspiration of the liquid remains a very delicate intervention because of the risk of the passage of the parasites in the blood circulation but the standard treatment is total or partial splenectomy followed by medical treatment based on albendazole 6, 7, 9, 10.
Conclusion
Splenic hydatid cyst is very rare, posing a real diagnostic dilemma with other cystic masses. However, the diagnosis of certainty remains the prerogative of the anatomo-pathological examination, especially since effective treatment remains on the prevention of this hydatid disease .
References
- 1.Shahriarirad R, Erfani A, Eskandarisani M, Rastegarian M, Sarkari B. (2020) Uncommon locations of cystic echinococcosis: a report of 46 cases from Southern Iran. Surg Res Pract. 206-1045.
- 2.Malik A A, Ul Bari S, Younis M, Wani K A, Rather A A. (2011) Primary splenic hydatidosis. , Indian 30, 175-177.
- 3.Rasheed K, Zargar S A, Telwani A A. (2013) Hydatid cyst of spleen: a diagnostic challenge. , N Am J Med Sci 5, 10-20.
- 4.Pukar M M, Pukar S M. (2013) Giant solitary hydatid cyst of spleen-a case report. , Int J Surg Case Rep 4, 435-437.
- 5.Kalinova K, Stefanova P, Bosheva M. (2006) Surgery in children with hydatid disease of the spleen. J Pediatr Surg. 41, 1264-1266.
- 6.Culafić D M, Kerkez M D, Mijac D D. (2010) Spleen cystic echinococcosis: clinical manifestations and treatment. , Scand J Gastroenterol 45, 186-190.
- 7.Farrokh D. (2013) Isolated primary splenic hydatid cyst in a six-year-old boy: a case report. Arch Clin Infect Dis. 8.
- 8.Singal R, Sandhu K S, Mittal A, Gupta S, Jindal G. (2016) A giant splenic hydatid cyst. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 29, 55-57.
